Packages and Classes
Probably the most important feature to grasp about ActionScript 3.0
is how to work with packages and
classes. In fact, your entire workflow initially
rests on your ability to recognize that you only deal with certain
features of ActionScript at any one time. For example, if you want to work
with a text field, you have to first import the TextField class from the flash.text package. Of course, you'll need to
know that the TextField class is in the
flash.text package, as well as where
other classes are stored. To get started, take a look at the script in
Example
1:
Example 1. (download this code sample at http://examples.oreilly.com/actionscript3qr)
package
{
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.text.TextField;
public class ShowText extends Sprite
{
public function ShowText():void
{
var actionText:TextField=new TextField();
var msg:String="Hello ActionScript 3.ohhhhh";
actionText.text=msg;
this.addChild(actionText);
actionText.width=((msg.length)*12)+4;
actionText.height=16;
actionText.x=200;
actionText.y=150;
}
}
}Save the script as ShowText.as.
To test this script, use the following steps:
Open a new Flash document, and in the Document class window in the Properties panel, type in the class name,
ShowText, as shown in Figure 1.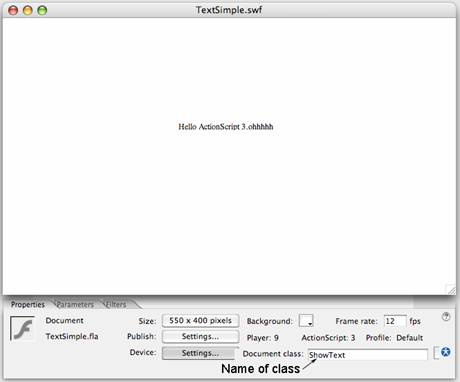
Figure 1. The script is associated with the Flash document through the Document class
Save the Flash document as
TextSimple.flain the ...
Get ActionScript 3.0 Programming: Overview, Getting Started, and Examples of New Concepts now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

