Chapter 20. web.config Reference
ASP.NET
provides a completely new model for configuring web applications.
This greatly simplified process makes it considerably easier to
deploy application configuration settings, the
application’s content, and its components. Central
to this new configuration model is web.config, an XML-based file that contains
the configuration settings for your application. Because the file is
written in XML, it is both human- and machine-readable.
web.config files configure
applications hierarchically -- i.e., an application can contain
more than one web.config file,
with each file residing in a separate folder of the application.
Settings in a web.config file in
a child folder of the application root override the settings of
the
web.config file in the parent folder.
Settings not defined in the child web.config file inherit the settings from the
parent web.config file. Figure 20-1 demonstrates these rules of precedence.
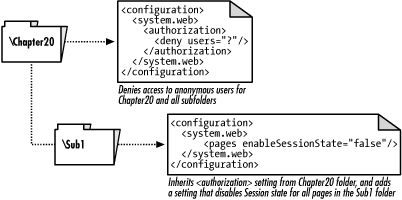
Figure 20-1. Inheriting and overriding web.config settings
In addition to inheriting settings from a web.config file defined in a parent folder,
all applications on a given machine inherit settings from a file
called machine.config. The
machine.config file contains
default ASP.NET configuration settings, as well as settings for other
.NET application types. Thus, in Figure 20-1, the
Chapter20 folder inherits the machine.config setting for the ...
Get ASP.NET in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

