Name
equal_range function template — Finds all occurrences of a value in a sorted range using binary search
Synopsis
template<typename FwdIter, typename T>
pair<FwdIter, FwdIter>
equal_range(FwdIter first, FwdIter last, const T& value);
template<typename FwdIter, typename T, typename Compare>
pair<FwdIter, FwdIter>
equal_range(FwdIter first, FwdIter last, const T& value, Compare comp);The equal_range function
template determines where value
belongs in the sorted range [first, last). It returns a pair of iterators that
specify the start and one past the end of the range of items that
are equivalent to value, or both
iterators in the pair point to where you can insert value and preserve the sorted nature of
the range.
The first form compares values using the < operator. The second form calls
comp(*iter, value).
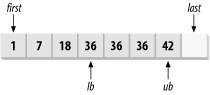
Figure 13-4 shows
how bounds are found with the value 36. The result of calling equal_range is pair(lb, ub). Note that for values in the range
[19, 35], the upper and lower bound are both
equal to lb, and for values in
the range [37, 41], the upper and lower bound are both
equal to ub.
 |
Technical Notes
Precondition: !(*(i + 1) < *i) for all i in [first, last - 1).
The equal_range function
template returns the equivalent of calling the following, although
the actual implementation might be different:
std::make_pair(std::lower_bound(first, ...
Get C++ In a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

