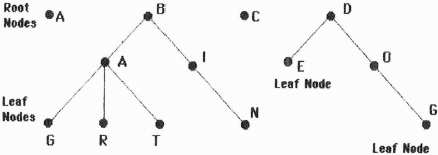
Figure 4.56 V.42 tree-based dictionary representation
Each of the leaf nodes shown in Figure 4.56 represents a node that has no other dependent nodes, in effect, representing the last character in a string. Conversely, a node that has no parent is known as a root node and represents the first character in a string.
Initially, each tree in the dictionary consists of a root node, with a unique codeword assigned to each node. As data is received from an attached DTE a string matching process occurs in which a sequence of DTE originated characters is matched against the dictionary. This process begins with a single character. If the string matches a dictionary entry and the entry was not created since the last invocation of the string matching procedure, the next DTE originated character is read and appended to the string. This process is repeated under the previously described conditions until the maximum string length is reached or the string does not match a dictionary entry or matches an entry created since the last invocation of the string matching procedure. At that time the last character appended to the string is removed and represents an ‘unmatched’ character while the characters in the string are encoded as a codeword.
Under V.42 bis the maximum string length can range from 6 to 250 and is negotiated between modems. The number of codewords has a default value of 512, which ...
Get Data Communications Networking Devices: Operation, Utilization and Lan and Wan Internetworking, 4th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

