3.2. Kinetic wind energy
A wind tube, at a speed v, contains a certain amount of the kinetic energy that the wind turbine receiving the section of this tube will convert into mechanical energy. To calculate it, we consider an air tube of length dl, section S and density ρ , which is driven by a speed v in accordance with Figure 3.8.
Figure 3.8. Air tube in motion
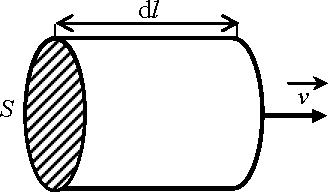
As for any solid in motion, the kinetic energy of this tube is expressed by the following expression:
[3.3] ![]()
m represents the total mass of the air volume that is contained in the tube. This mass depends on the length of the considered volume, which can be expressed by using the air density (ρ):
[3.4] ![]()
with dl = vdt
The air density depends on the pressure p, on the specific ideal gas constant Ra and on the air temperature ![]() , with for a dry air, Ra =287,058 J.kg−1.K−1 and p =101,325 kPa. For a given location of the wind turbine, temperature is the main parameter fluctuating throughout the year; this leads to density variations. Under normal temperature and pressure conditions, ρ = 1,225 kg/m3. Given that this mass moves at speed ...
, with for a dry air, Ra =287,058 J.kg−1.K−1 and p =101,325 kPa. For a given location of the wind turbine, temperature is the main parameter fluctuating throughout the year; this leads to density variations. Under normal temperature and pressure conditions, ρ = 1,225 kg/m3. Given that this mass moves at speed ...
Get Electricity Production from Renewables Energies now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

