CHAPTER 4 FORMS OF BUSINESS OWNERSHIP
One of the basic and early decisions a new business owner has to make is choosing the legal form of business ownership and organization. The legal form of business is not only related to business nature or the owner's desire but also to its significance in terms of the long-term implications on business performance and survival. In the choice process, an owner has to be aware and knowledgeable of the pros and cons of each and every form of business, and preferably be assisted by a lawyer and business consultant. Among the issues that will be affected by the choice of the form of ownership are the taxes, liabilities, succession, capital raising, control, reinvestment, income-growth allocation, business fate and survival, and the like. The final decision would be in the owner's hands, and ultimately the right decision would be the one that results in choosing the form which is the most fitting to that particular business and the circumstances around it. The major forms of business, which we discuss here, are: the sole proprietorship, partnership, and corporation in addition to other hybrid or sub-forms that will be covered briefly too. Figure 4.1 shows the distribution of major forms of business.
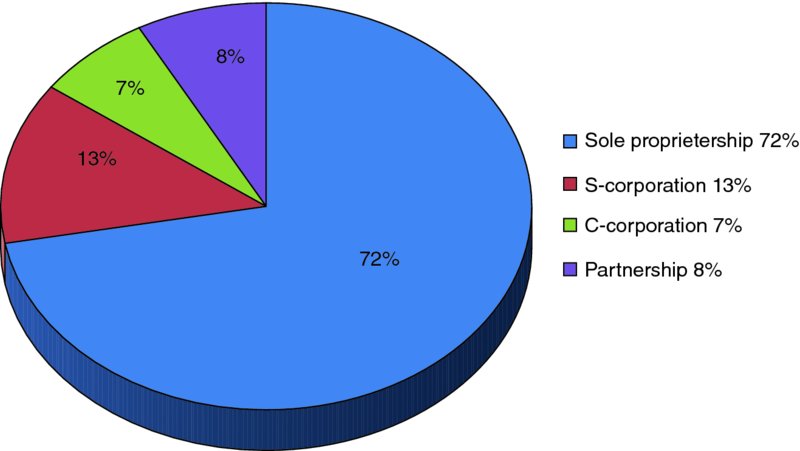
Figure 4.1 Distribution
4.1 Sole Proprietorship
Sole proprietorship is the business owned and managed by a single person. The vast majority ...
Get Entrepreneurial Finance: Fundamentals of Financial Planning and Management for Small Business now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

