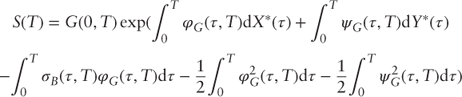Chapter 30Pricing of Energy Derivatives
Unpublished memorandum, 2002.
It was shown in Geman and Vasicek (2001) (Chapter 29 of this volume) that the price ![]() of a forward contract maturing at T is subject to
of a forward contract maturing at T is subject to
where ![]() are Wiener processes under a risk-neutral probability measure
are Wiener processes under a risk-neutral probability measure ![]() equivalent to P.
equivalent to P.
Integrating Eq. (1) from 0 to T and taking into account that ![]() yields
yields
Eq. (2) represents a complete specification of the forward/spot process. It is fully described by the forward contract volatilities, and it only includes processes whose stochastic properties under the measure P* are known. Therefore, the prices of energy derivatives and contingent claims can be calculated without recourse to the market prices of risk, which are not directly observable. In this sense, it is akin to the Heath/Jarrow/Morton (1992) model of interest rates (their Eq. (26)).
The price of any derivative contract (e.g., ...
Get Finance, Economics, and Mathematics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.