The essence of the 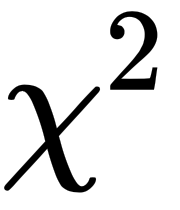 test is a threshold value based on the number of degrees of freedom and the level of uncertainty we're willing to entertain in accepting or rejecting the null hypothesis. Conventionally, we're advised to use a threshold around 0.05 (1/20) to reject the null hypothesis. We'd like there to be only 1 chance in 20 that the data is simply random and it appears meaningful. In other words, we'd like there to be 19 chances in 20 that the data reflects simple random variation.
test is a threshold value based on the number of degrees of freedom and the level of uncertainty we're willing to entertain in accepting or rejecting the null hypothesis. Conventionally, we're advised to use a threshold around 0.05 (1/20) to reject the null hypothesis. We'd like there to be only 1 chance in 20 that the data is simply random and it appears meaningful. In other words, we'd like there to be 19 chances in 20 that the data reflects simple random variation.
The chi-squared values are usually provided in tabular form because the calculation involves a number of transcendental ...

