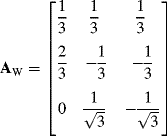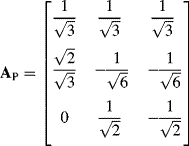9.2 Three-phase to Two-phase Transformations
For a deeper analysis of electric drives with filters, knowledge of filter models is required.
The natural frame of co-ordinates for a three-phase system is a three-axis co-ordinate with a 120-degree shift, but for a better analysis of the system, the use of the orthogonal co-ordinates is more useful, as well as easier to understand. Therefore, for the next analysis, proper co-ordinate transformations are presented. Two kinds of transformations are used, one for constant vectors magnitudes and another for constant power of the three-phase and two-phase frames of reference.
The transformation matrix for the conversion from a three-phase ABC co-ordinate to a two-phase αβ0 co-ordinate for constant vector magnitude is described as
and the transformation matrix for constant power of the system is
Using equations (9.1) or (9.2), each of the model variables x can be transformed from ABC to two-phase αβ0 co-ordinates according to
(9.3) 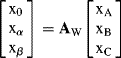
where the variables retain the same magnitude in each co-ordinate.
The next relation is used when the constant power of both systems is fulfilled:
(9.4)
The parameter transformations are required for ...
Get High Performance Control of AC Drives with Matlab / Simulink Models now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.