6 Voice Evolution
Harri Holma and Karri Ranta-aho
6.1 Introduction
Circuit Switched (CS) voice was part of the WCDMA offering from Day 1 together with the Packet Switched (PS) data service. WCDMA voice uses Adaptive Multirate (AMR) codec with a data rate of 12.2 kbps. In many developed countries more than 50% of mobile voice minutes are now carried by WCDMA CS voice. The voice is still important from the operator revenue point of view even if data traffic is far higher than voice from the volume point of view. The voice service keeps improving further: AMR wideband (AMR-WB) offers High Definition (HD) quality, lower rate AMR improves voice capacity, voice-over HSPA provides both VoIP and CS voice capability, CS fallback from LTE to WCDMA CS voice enables voice services for LTE smartphones, and Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC) brings handover from VoIP to CS voice. These evolution steps are summarized in Figure 6.1 and described in more detail in this chapter.
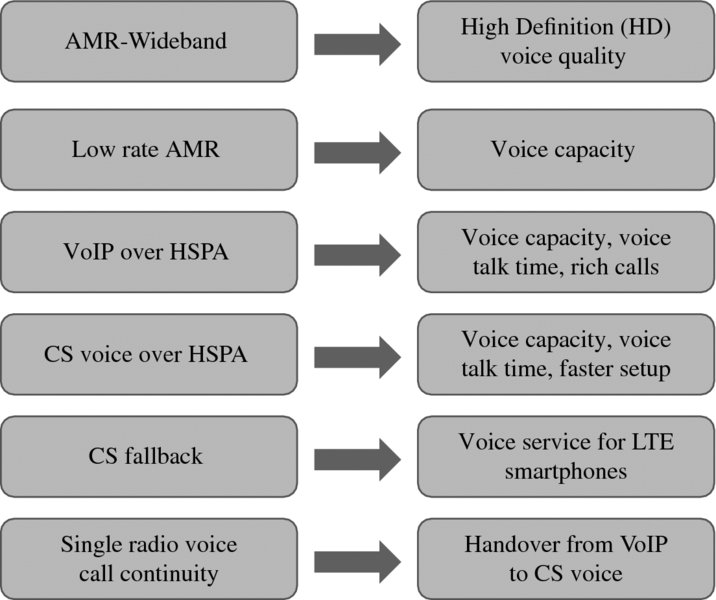
Figure 6.1 Voice enhancement options in WCDMA/HSPA
6.2 Voice Quality with AMR Wideband
AMR Wideband (AMR-WB) enhances voice quality by a higher voice sampling rate in voice encoding. AMR Narrowband (AMR-NB) uses an 8 kHz sampling rate which enables an audio bandwidth of 300–3400 Hz, similar to traditional landline phones. AMR-WB uses 16 kHz which increases the audio bandwidth to 50–7000 Hz. Voice sounds ...
Get HSPA+ Evolution to Release 12: Performance and Optimization now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

