A* Taking Diagonal Moves into Account
For Example 8-15, we will be making changes to Example 8-14 to add in diagonal movement to the A* path.
So far, each of our examples has used the astar.js functions, which ignore diagonal
movements between nodes. We can easily add this capability. Example 8-15 does this with one
simple change. We will be changing the false in the A* search function to true:
//For example 8-15 we will add true to the end of the search functionvarresult=astar.search(graph.nodes,start,end,true);
By simply changing false to
true at the end of the call to the astar.search(), we can change the result node
path dramatically. Figure 8-15 shows the path
difference.
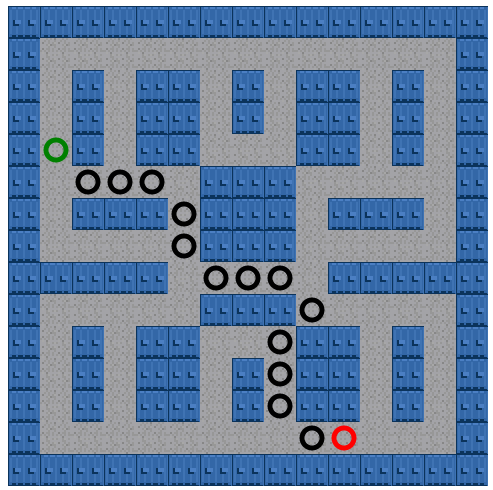
Figure 8-15. A* applied to the 15x15 tile map with diagonals
Each node on the movable tiles has the same weight (1). When A* calculates the shortest node path,
it does so by taking these weights into account. Next we will add in
some nodes with a higher weight value.
Example 8-15. Larger A* example with diagonals
<!doctype html><htmllang="en"><head><metacharset="UTF-8"><title>Chapter 8 Example 15 - Larger A* Example with Diagonals</title>
<scriptsrc="modernizr.js"></script><scripttype='text/javascript'src='graph.js'></script><scripttype='text/javascript'src='astar.js'></script><scripttype="text/javascript">window.addEventListener('load',eventWindowLoaded,false);functioneventWindowLoaded() ...
Get HTML5 Canvas, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

