Forming Processes
4.1 Forging
Process Description
Hot metal is formed into the required shape by the application of pressure or impact forces causing plastic deformation using a press or hammer in a single or a series of dies (Figure 4.1(a)).
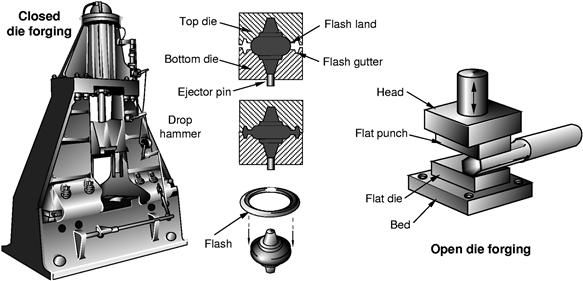
Figure 4.1(a) Forging.
Materials
• Mainly carbon; low alloy and stainless steels; aluminium; copper; and magnesium alloys. Titanium alloys, nickel alloys, high alloy steels and refractory metals can also be forged.
• Forgeability of materials important; must be ductile at forging temperature. Relative forgeability is as follows, with easiest to forge first: aluminium alloys, magnesium alloys, copper ...
Get Manufacturing Process Selection Handbook now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

