3.2 2G
Since the inception, 2G system has evolved with new functionalities during the years and standardization releases. So for discussion on further detail of the system capabilities, one needs to consider the 3GPP release to which the system complies with. Initially in 2G, the focus was on providing mobile voice service. One technological difference compared to the previous ‘1G’ systems is that in 2G voice and all services are digital, not analogue. For further reading on 2G see [12] and [13].
Enhancements in the 2G network include AMR (Adaptive Multi-Rate) speech, high speed circuit switched data (HSCSD), GPRS (General packet radio service), and EDGE (Enhanced data rates for global evolution). Term GERAN (GSM/EDGE Radio access network) is used to refer to the 2G radio access network with these enhanced capabilities. GERAN also includes an Iu-interface option, which is inherited from the 3G system. Mobile stations may then operate either in A/Gb mode or in Iu mode, depending on how the 2G radio access network interfaces the core network.
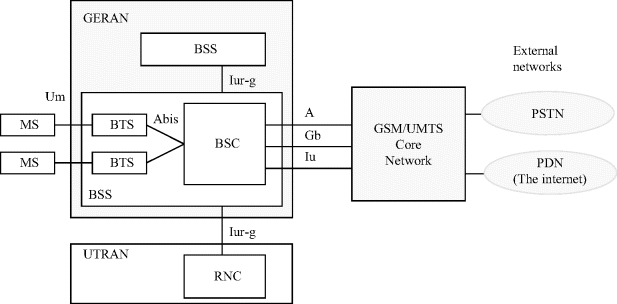
The system architecture of the GERAN network is shown in Figure 3.4. The base station subsystem (BSS) internal interface between the BTS and the BSC is Abis.
Figure 3.4 GERAN structure [12].
3.2.1 Circuit Switched Traffic
Figure 3.5 shows the GERAN user plane with both A-mode and Iu mode interfaces. The initial 2G (A-mode) protocols are indicated ...
Get Mobile Backhaul now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

