Chapter 1
Basis of the TLM Method: the 2D TLM Method
1.1. Historical introduction
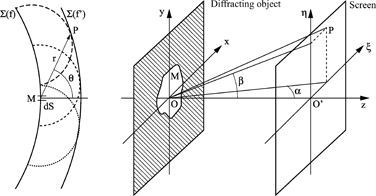
Historically, this method is based on the Huygens–Fresnel principle, which states that each point of a wave front can be considered to be an isotropic, spherical, a secondary source, and the energy is isotropically distributed in all directions, as illustrated in Figure 1.1.
Figure 1.1. Huygens’ principle
The 2D TLM method was formulated by Johns in 1971, based on the principles outlined below.
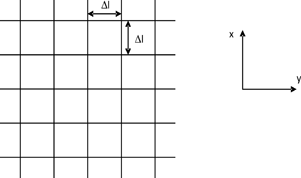
Space is modeled using a Cartesian matrix of points or nodes separated by a gap Δl, where Δt represents the time taken for a pulse to travel from one node to another.
Figure 1.2. Transmission line network in the XY plane
Johns [JOH 71] applied this principle in order to solve electromagnetic problems and create secondary sources by connecting transmission lines, regularly spaced in a series or in parallel.
If a Vo=1V Dirac pulse is applied to any branch of this parallel node, propagating to node A, we obtain:
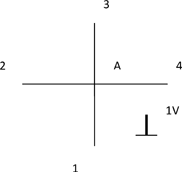
If every branch of the node has the same characteristic impedance Zc, then the impedance “seen” by the incident pulse will be equal to Zc/3 and will be reflected with a coefficient:
[1.1]
The voltages ...
Get Numerical Analysis in Electromagnetics: The TLM Method now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

