3.6 PHOTOCOUNTING WITH RANDOM PHOTOMUL TIPLICATION
When a photomultiplier is used to enhance the electron flow, the randomness of the photomultiplication mechanism will influence the statistics of the output count. If we let k1 be the electron count over a volume based on primary electron flow (as computed in Section 3.1) then the output count k2 (number of total output electrons that flow after photomultiplication) will have a probability
![]()
Here P(k1) is the primary count probability, and P(k2|k1) is the conditional output count probability conditioned on a k1 primary count. This conditional count depends on the type of photomultiplier used and the mechanism that generates the secondary emissions.
With a PMT having mean gain ![]() , the conditional probability is generally modeled as
, the conditional probability is generally modeled as
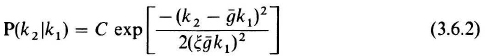
where C is a normalizing factor. Equation (3.6.2) is a Gaussian-shaped count envelope (recall k2 only takes on integer values) centered at ![]() , with a deviation spread of
, with a deviation spread of ![]() , with ξ the PMT spreading factor. The resulting ...
, with ξ the PMT spreading factor. The resulting ...
Get Optical Communications, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

