2 Derivation of the Uncertainty Principle
Consider a sinusoidal wave along the
x
‐axis having amplitude
a
and wavelength
λ
. Its corresponding wave number
k
is defined as ![]() . We can express the wave as
. We can express the wave as
If an electron is described by this wave it will have infinite spatial extent. A spatially localised wave packet may be obtained mathematically by adding a series of component sinusoidal waves together, each sinusoidal wave having a unique wavelength. This forms a Fourier series.
Consider the following sum of waves
This may be written as an integral in the case of a continuum of wavelengths:
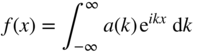
Assume, for simplicity, that only a range of wavelengths of the component waves exists such that
and outside of this range a(k) = 0.
Now we obtain
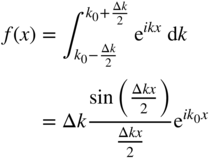
The amplitude of this wave is now in the form of a sinc function. We will approximate the width of the sinc function ...
Get Principles of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

