Chapter 11. Decision Tree Analysis
Decision tree analysis is a useful tool for determining the expected value of an investment or any decision where there are multiple outcomes possible. For example, a company is looking to expand its business and has several possibilities for proceeding:
Build a new facility.
Renovate a current facility.
Buy a facility from a competing company that is forced to sell due to an impending bankruptcy.
Do nothing and maintain the status quo.
The decision tree is built with each possibility following a separate path in the tree with the final expected values at the end of the process. The drawing in Figure 11.1 is a highly simplified version of a decision tree chart.
The interesting aspect of this type of decision process is that there is always the option to do nothing in reference to the other options. If none of the options look like they will produce the desired result, it may be better to do nothing at all or rethink the problem from a different point of view.
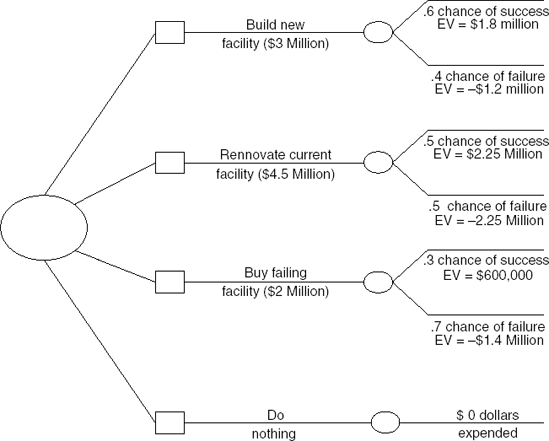
Figure 11.1. Figure 11.1
One critical aspect of decision tree analysis is that you are required to estimate the anticipated probability that an event will occur—these estimates are represented by numbers next to each "chance of success" phrase on the diagram. How well you perform these estimates will render the decision tree analysis either accurate or flawed. This is why it may be necessary to spin ...
Get Real-World Project Management: Beyond Conventional Wisdom, Best Practices, and Project Methodologies now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

