Event Management
Windows keeps a system log that is a record of events that take place on the computer. Examples of such events include:
Device driver problems
Hardware errors
Logins and logouts
Reboots
Service startups and shutdowns
Creation of, and changes of, user accounts
Program errors
These events and more are kept in the event log and are viewable with the Event Viewer. But before I talk about that, let's go into more detail on auditing, which also results in event log entries.
Manage Auditing
Auditing gives you the ability to watch certain types of events even more closely.
Note
Microsoft uses the terms "events" and "audit" in the same context. Audit log entries and event log entries are the same thing.
Turn on auditing
Follow these steps to turn on auditing:
Go to Control Panel → System and Maintenance → Administrative Tools.
Double-click 'Local Security Policy.' The 'Local Security Policy' window appears, as in Figure 15.
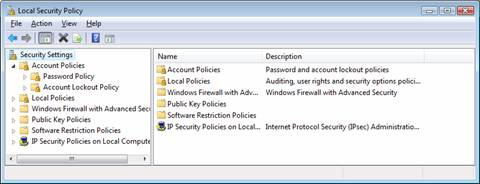
Figure 15. The 'Local Security Policy' window is the path to many security policy functions including auditing
Open Local Policies → Audit Policies. Click 'Audit Policies.' The window should now appear like Figure 16.
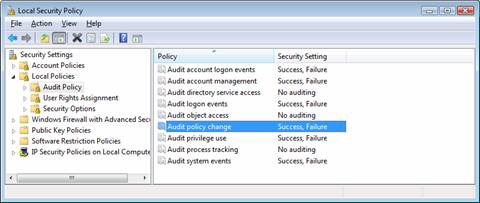
Figure 16. Viewing and setting Audit Policies
Double-click the Audit Policy you wish to change. For instance, you may wish to turn on auditing for privilege use. ...
Get Securing the Vista Environment now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

