11.7 SLOW-DOWN, RETIMING, AND PIPELINING
Many useful realizations contain nodes that are not connected to unit-delay branches. These nodes or variables thus do not appear in a state variable description and the scaling and noise computation methods cannot be applied directly. To overcome this difficulty, the SRP (slow-down and retiming/pipelining) transformation technique (see chapters 4 and 3) can be used as a preprocessing step.
Consider the filter in Fig. 11.19(b) which is obtained by applying slowdown transformation (M = 3) to the filter in Fig. 11.19(a). By 3 slow-down transformation, every z-variable in Fig. 11.19(a) is changed into z3. Thus the transfer function of the transformed filter H′(z) is related to the original transfer function H(z) as
![]()
Thus, if the unit-sample response from the input to the internal node x in Fig. 11.19(a) is defined by
![]()
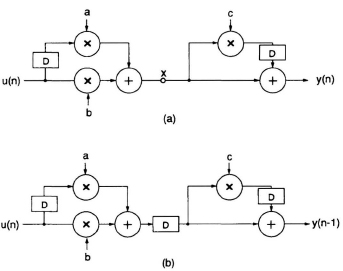
Fig. 11.20 (a) A filter with a nonstate variable node on a feed-forward path. (b) Nonstate variable node is converted into state variable node by pipelining.
the unit-sample response from the input to the internal node x′ in Fig. 11.19(b) is
Then,
Similarly, it can be shown that
The foregoing analysis shows that slow-down ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

