17.5 POWER REDUCTION TECHNIQUES
Power optimization refers to the problem of reducing power consumption in a digital circuit at various abstractions of the design − from the software and algorithmic level down to the layout level. Traditional algorithmic transformations like pipelining and parallel processing can be used to reduce power consumption by operating the system with lower supply voltage (see Chapter 3). Power consumption can also be reduced by reducing capacitance by strength reduction transformation, either at the algorithmic level (see Chapter 9) or at the numerical level (see Chapter 15). In this section, some of the more recent techniques are briefly discussed.
17.5.1 Path Balancing
In order to reduce the glitching activity in a circuit, the delay of all true paths that converge at each gate must be roughly balanced, because path balancing leads to nearly simultaneous switching on the various gate inputs, and thus eliminates possible hazards at the output of the gate as shown in Fig. 17.8. This in turn reduces the average power dissipation in the circuit. Path balancing can be achieved before or after technology mapping. Before technology mapping it is achieved by logic decomposition or selective collapsing. After technology mapping it is achieved by delay insertion and pin reordering.
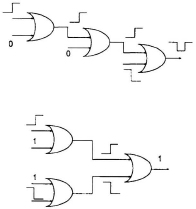
Fig. 17.8 Example illustrating the effect of path balancing.
The idea behind ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

