Encryption
Encryption alters the bits of each data packet to guard eavesdroppers from decoding data, such as credit card numbers. Before encryption the data is called plaintext, which is easy to decode by using sniffing tools. The encryption converts the plaintext into ciphertext, which someone can decode only through the use of a proper secret key.
Many encryption methods, such as the 802.11 Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), are symmetric—that is, the same key that does the encryption is also the one that performs the decryption. Figure 8-4 illustrates this process.
Figure 8-4. Symmetric Encryption Uses a Common Key
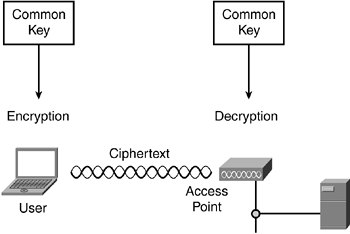
For example, the radio NIC uses ...
Get Wireless Networks first-step now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

