Name
Table → Sort
Synopsis
Many tables are designed to look (and perhaps operate) like mini-databases. A list of records, one in each row, topped by a row of column headings that identify the components of each row (functioning as database fields) is a typical arrangement. The Table → Sort command (Figure 10-23) sorts rows by up to three column headings within a table.
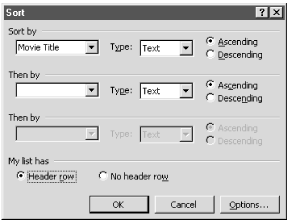
Figure 10-23. Sorting the rows of data in a table
Click the first Sort by list box and choose the column heading on which to sort a table’s rows. Once the first Sort by box is set, use the others to apply additional levels of sorting. For example, you could sort a list of contacts first by state and then by city. For each sort performed, choose Ascending for an alphabetical sort or Descending for a reverse alphabetical sort.
If the lists display columns as Column 1, Column 2, etc., click the Header row option at the bottom of the dialog box. This tells Word to use the contents of the cells on the top row of the table for sorting. This also tells Word not to include the header row in the actual sort.
The Options button on the Sort dialog opens a separate dialog with additional options. Use it to:
Set delimiters when sorting non-tabular text (see Use Table )
Set a language for the sort
Make capitalized words come before lowercased words in a sort
Sort only a selected column instead of the whole table
Use Table → Sort on Non-Tabular ...
Get Word 2000 in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

