Bots: What you need to know
Bots are made possible by recent advances in artificial intelligence, user interface, and communication.
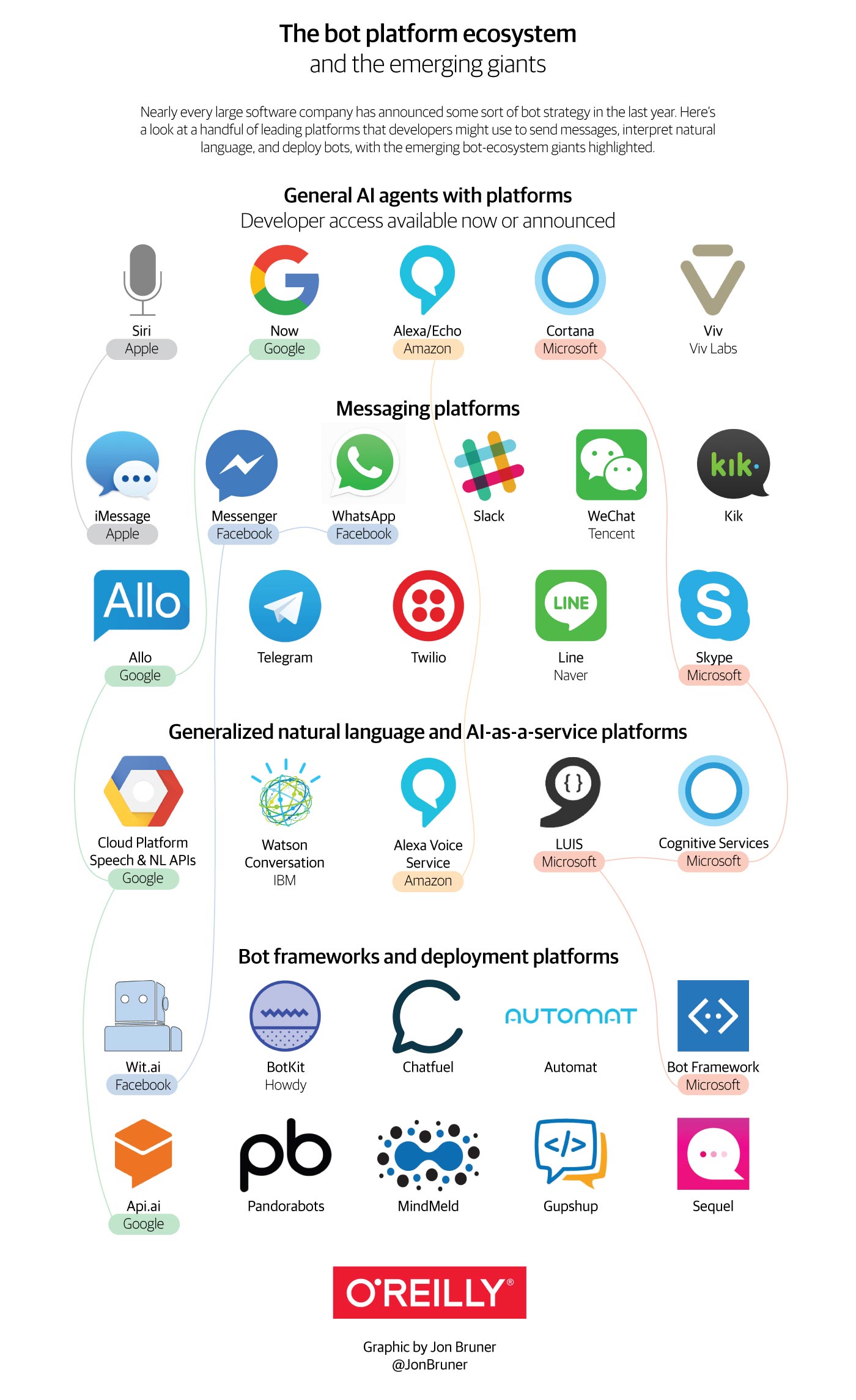
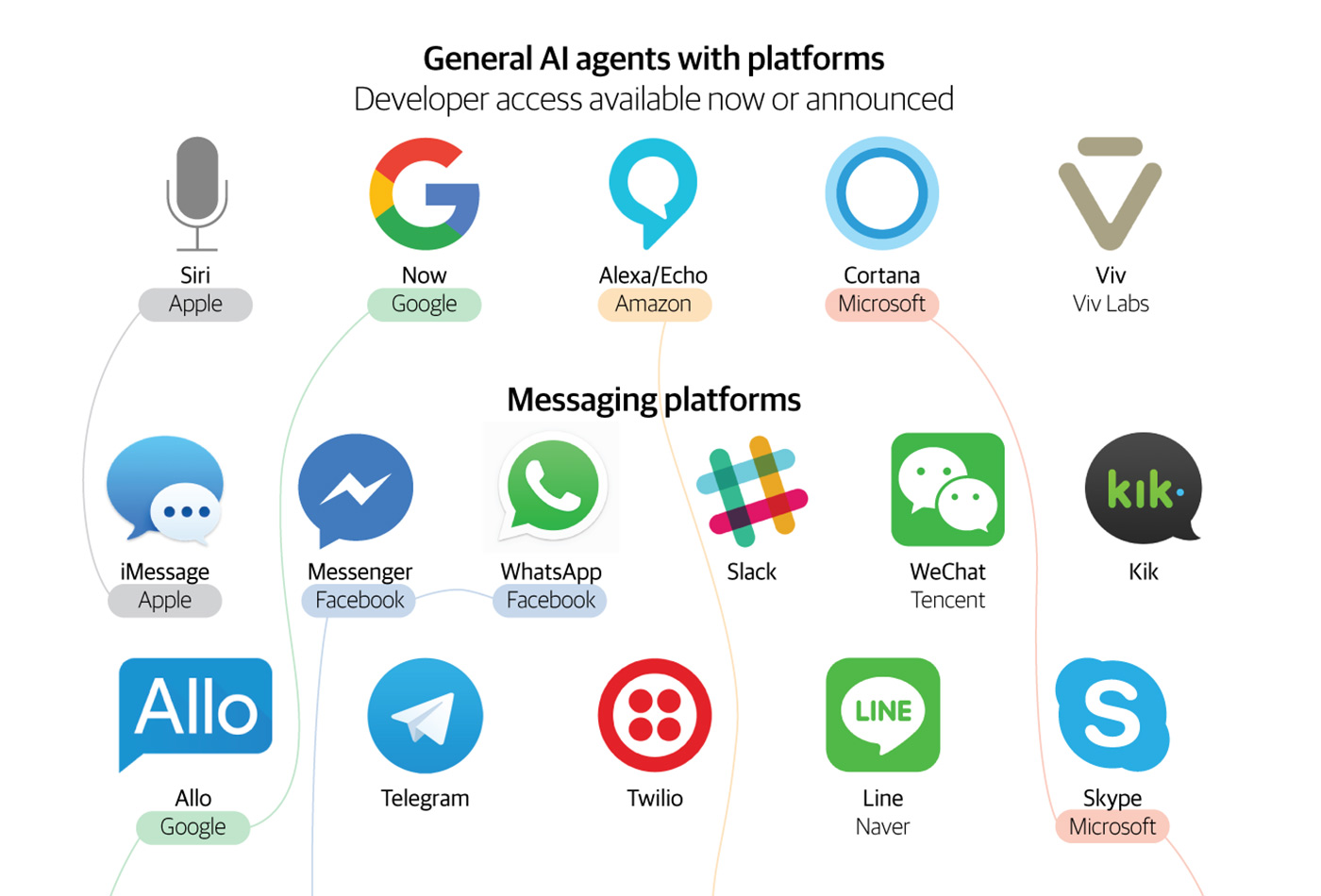 Bots landscape. (source: O'Reilly)
Bots landscape. (source: O'Reilly)
“Bots are the new apps”—Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft
Bots are a new, AI-driven way to interact with users in a variety of environments. As AI improves and users turn away from single-purpose apps and toward messaging interfaces, they could revolutionize customer service, productivity, and communication.
Getting started with bots is as simple as using any of a handful of new bot platforms that aim to make bot creation easy; sophisticated bots require an understanding of natural language processing (NLP) and other areas of artificial intelligence.
Bots use artificial intelligence to converse in human terms, usually through a lightweight messaging interface like Slack or Facebook Messenger, or a voice interface like Amazon Echo or Google Assistant. Since late 2015, bots have been the subject of immense excitement in the belief that they might replace mobile apps for many tasks and provide a flexible and natural interface for sophisticated AI technology.
Bots are promising for a number of use cases currently served by mobile apps, as well as many that have never been well served by mobile apps:
- Customer relationship management: consumer-facing bots can assist customers with difficult transactions, make recommendations, and gather data. For instance, an airline’s bot could answer questions about fees, rebook flights, and suggest add-ons like hotel and car reservations. Matched to a sophisticated data-mining back end, the bot could build up customer profiles that the airline can use to market vacations, travel deals, and additional services.
- Productivity: bots could replace many slow tasks with a simple natural-language interface. For instance, a bot connected to an electronic medical record system could retrieve information faster than a conventional lookup; just ask “what was the patient’s blood pressure during his January visit?” Bots are already able to schedule meetings over email, retrieve reports from analytics systems, and facilitate communication among teams.
- Publishing and entertainment: bots provide an engaging, highly dynamic interface for many kinds of content. The New York Times and Quartz, for instance, both offer bots that display articles in a conversational format. Other publishers have experimented with conversational novels, video, and magazine content sent directly to users through popular messaging platforms. Bots are a particularly promising way to reach younger users, many of whom spend enormous amounts of time in messaging apps like Kik, and could be a significant avenue for influencer marketing.
Conversational bots are a response to several larger trends that are reshaping communication and mobile computing:
- The mobile app economy is stagnating; it’s getting harder to persuade consumers to download and use new apps. As The Economist pointed out: “The 20 most successful developers grab nearly half of all revenues on Apple’s App Store. Building apps and promoting them is getting more costly. Meanwhile, users’ enthusiasm is waning, as they find downloading apps and navigating between them a hassle. A quarter of all downloaded apps are abandoned after a single use.”
- Consumers like conversational interfaces, and companies want to make themselves available on the platforms that their customers enjoy using. Facebook Messenger is the most popular Android app; it and WhatsApp (another Facebook messaging app) each have more than one billion active users.
- Artificial intelligence has advanced remarkably in the last three years, and is reaching the point where computers can have moderately complex conversations with users in natural language. Plus, AI-as-a-service is beginning to become available, making it possible for developers without deep learning expertise to implement AI in their software.
Bot platform overview
Chatbots have been around since at least the 1960s, but they took off in the spring and summer of 2016 as Facebook, Microsoft, Slack, Google, and Apple announced powerful platform features that encourage chatbot development. Several of those companies have built a comprehensive bot stack, consisting of a messaging platform, an artificial intelligence service, and a conversational framework.
Several of these stacks also offer a central AI agent like Siri, Google Now, or Alexa that ties services together and could eventually operate as a “god bot” that dispatches work to other bots (for instance, opening the Uber bot when you say “Alexa, call me a car.”)
The graphic below summarizes the major bot stacks as of September 2016.
Learn more about bots
Start building bots with resources from Safari. Begin with an overview of the field—enough to start building simple bots—then move into more advanced topics like natural language processing (NLP).
Overviews
What are Conversational Bots? by Jon Bruner and Mike Barlow, provides a high-level survey of applications and ecosystem players.
The Bot Day Video Compilation offers a series of introductions covering AI, design, platforms, user experience, and applications.
Conversational UI design
The discipline of bot UI design is brand new, and significantly different from traditional web UI design. Two leading authorities on conversational user interfaces have written books on the topic for O’Reilly:
- Designing Bots, by Amir Shevat.
- Designing Voice User Interfaces, by Cathy Pearl.
Introductory AI
Deep learning is one of the enabling developments in artificial intelligence that has enabled the rise of bots. Start learning about deep learning with our Deep Learning Video Collection.
If you want to start coding right away, try Fundamentals of Deep Learning, by Nikhil Buduma. It includes a strong introduction to TensorFlow, a new deep learning library from Google that’s becoming a leading tool for AI developers. Or, for a very deep dive into machine learning, try Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn and TensorFlow, by Aurélien Géron.
Natural language processing (NLP)
NLP is the discipline concerned with making computers communicate in human terms.
For an introduction to NLP with modern Python-based techniques, watch Natural Language Text Processing with Python.
Or, register for Paco Nathan’s live training, Get Started with Natural Language Processing in Python, offered free to Safari subscribers.
If you’re interested in combining big data and NLP, try Building Pipelines for Natural Language Understanding with Spark, by Alex Thomas and David Talby.
