10Vector Control of Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives
10-1 Introduction
In the previous course [1], we looked at permanent-magnet synchronous motor drives, also known as “brushless-dc motor” drives in steady state, where without the help of dq analysis, it was not possible to discuss dynamic control of such drives. In this chapter, we will make use of the dq-analysis of induction machines, which is easily extended to analyze and control synchronous machines.
10-2 d-q Analysis of Permanent Magnet (Nonsalient-Pole) Synchronous Machines
In synchronous motors with surface-mounted permanent magnets, the rotor can be considered magnetically round (non-salient) that has the same reluctance along any axis through the center of the machine. A simplified representation of the rotor magnets is shown in Fig. 10-1a. The three-phase stator windings are sinusoidally distributed in space, like in an induction machine, with Ns number of turns per phase.
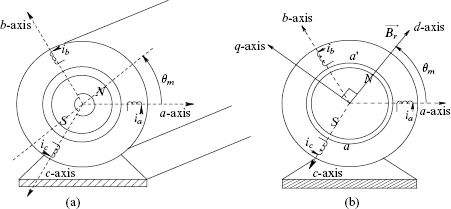
In Fig. 10-1b, d-axis is always aligned with the rotor magnetic axis, with the q-axis 90° ahead in the direction of rotation, assumed to be counter-clockwise. The stator three-phase windings are represented by equivalent d- and q-axis windings; each winding has ![]() turns, ...
turns, ...
Get Advanced Electric Drives: Analysis, Control, and Modeling Using MATLAB/Simulink now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

