Introduction
What are Alternative Alternatives?
My working definition for this book has been based on unconventional, nontraditional, nonmainstream hedge fund investments and strategies whose risk profiles and return drivers are atypical, unique and/or idiosyncratic in nature.
Given that financial literature tends to define alternative investments as a negation to traditional assets or, in other words, if core asset classes include equities, bonds, real estate, commodities and currency, and if these are compounded by their respective derivatives, then alternative investments are the resulting permutations and combinations thereof – such as hedge funds, structured products, etc. If we were to take this thinking a step further, then ‘alternative alternatives’ could be considered a ‘negation’ of alternative investments.
Source: Sona Blessing
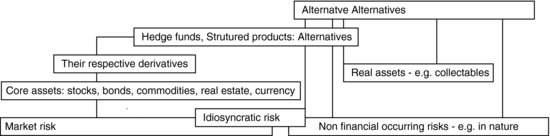
Why Alternative Alternatives?
The raison d'être for alternative alternatives and my hypothesis has been:
– In theory, market risk (also referred to as systematic risk or beta) can be isolated and measured.
– By default, a risk originating outside financial and capital markets (as in nature) should not be affected by it.
– Clearly, neither the biological growth of trees nor the occurrence of natural/weather phenomenon are influenced by events playing out in financial and capital markets. Quite simply, trees will continue to grow provided they ...

