Chapter 3. Writing Real-Time Applications for the IoT
Let’s look at examples of real-time applications for the IoT.
Case Study: Electronics Manufacturing in the Age of the IoT
A global electronics manufacturer of IoT-enabled devices was dealing with multiple streams of high-velocity inbound data. Figure 3-1 shows its architecture.
Event data from thousands to millions of devices—some mobile, some “smart,” some consumer appliances—arrived via the cloud to be processed by numerous apps, depending on the device type. Sitting between the data sources and the database tier (Cassandra, PostgreSQL, and Hadoop) was a rules engine that needed high-speed access to daily event data (e.g., a mobile device subscriber using a smart home app), which it held in an in-memory data grid used as an intraday cache.
As the rules engine ingested updates from the smart home application, it used the intraday data (such as location data on the device) from the in-memory grid to take actions (such as turn on lights when the mobile device wasn’t in the home).
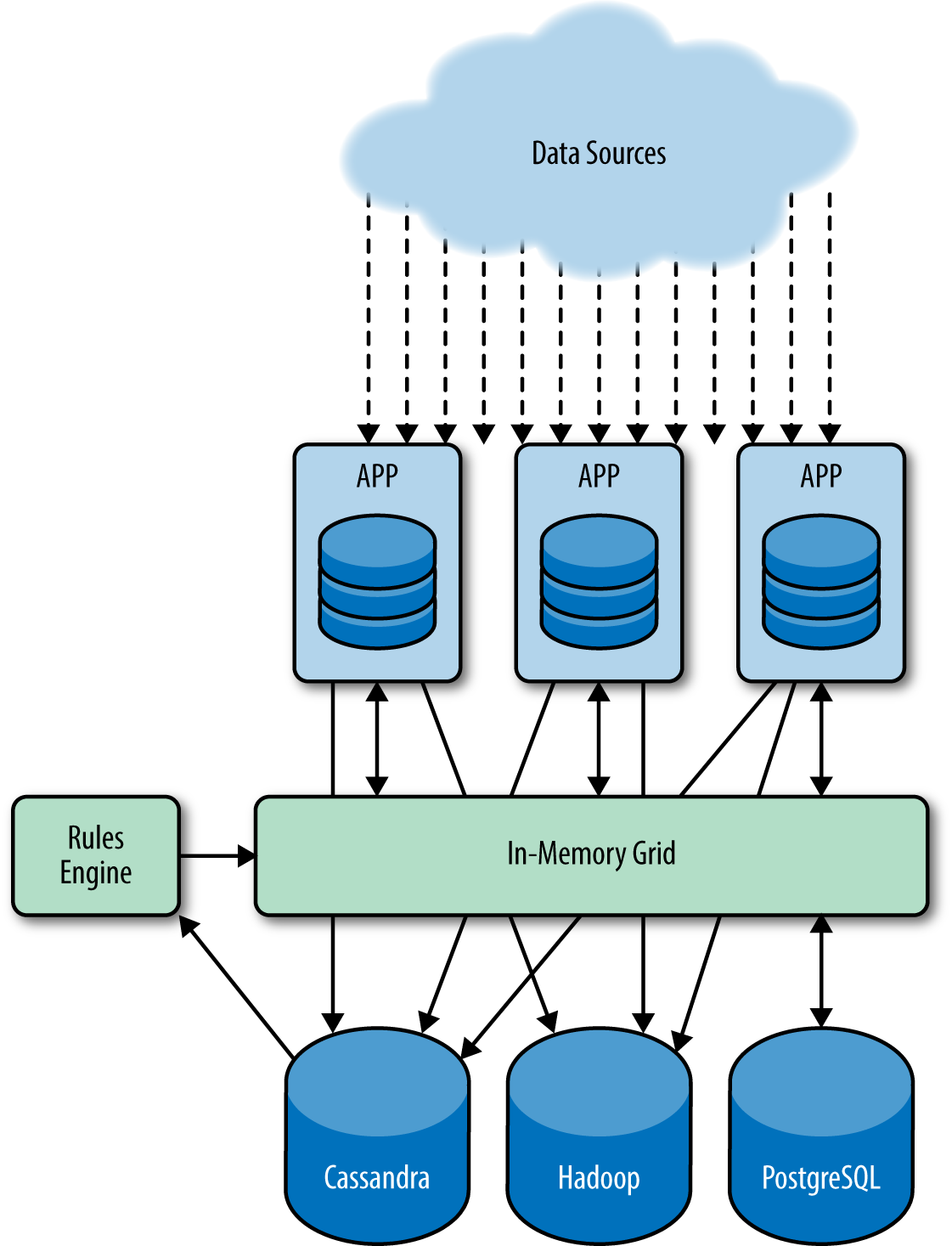
Figure 3-1. The architecture of a manufacturer of IoT-enabled devices
The rules engine queried Cassandra directly, creating latency and consistency issues. In some cases, the rules engine required stricter consistency than was guaranteed by Cassandra, for example, to ensure that a rule’s execution was idempotent. Scalability issues added to the problem—the ...
Get Architecting for the Internet of Things now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

