CHAPTER 43Functional Annotation of Common Differentially Expressed Genes
GVPPSR Kumar, AP Sahoo and A Kumar
Animal Biotechnology Division, IVRI, UP, India
43.1 INTRODUCTION
Cuffdiff predicts Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) and gives the gene symbols in the output. However, EBSeq, DESeq2, and edgeR give the output of DEGs in Ensembl IDs. These Ensemble IDs are initially converted into gene symbols using g:Convert in g:Profiler. After conversion, it is always better to identify commonly differentially expressed genes across all the packages and further proceed with the analysis. The commonly predicted genes are identified by using the Venny package.
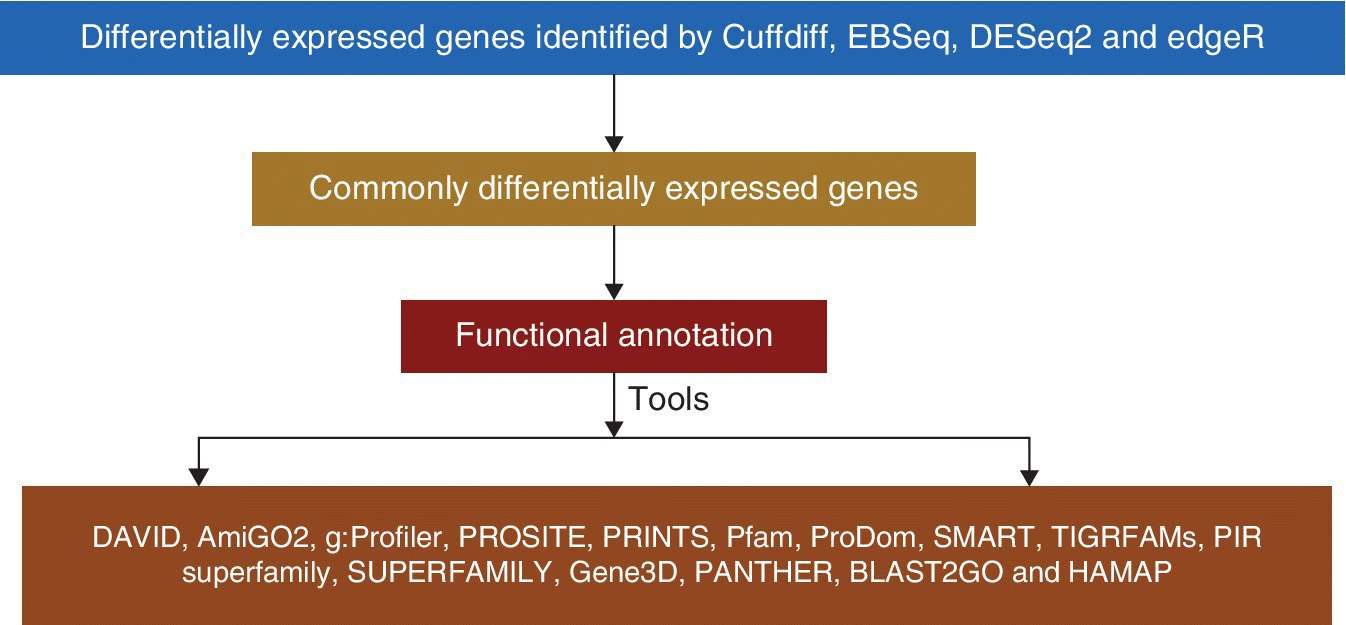
FIGURE 43.1
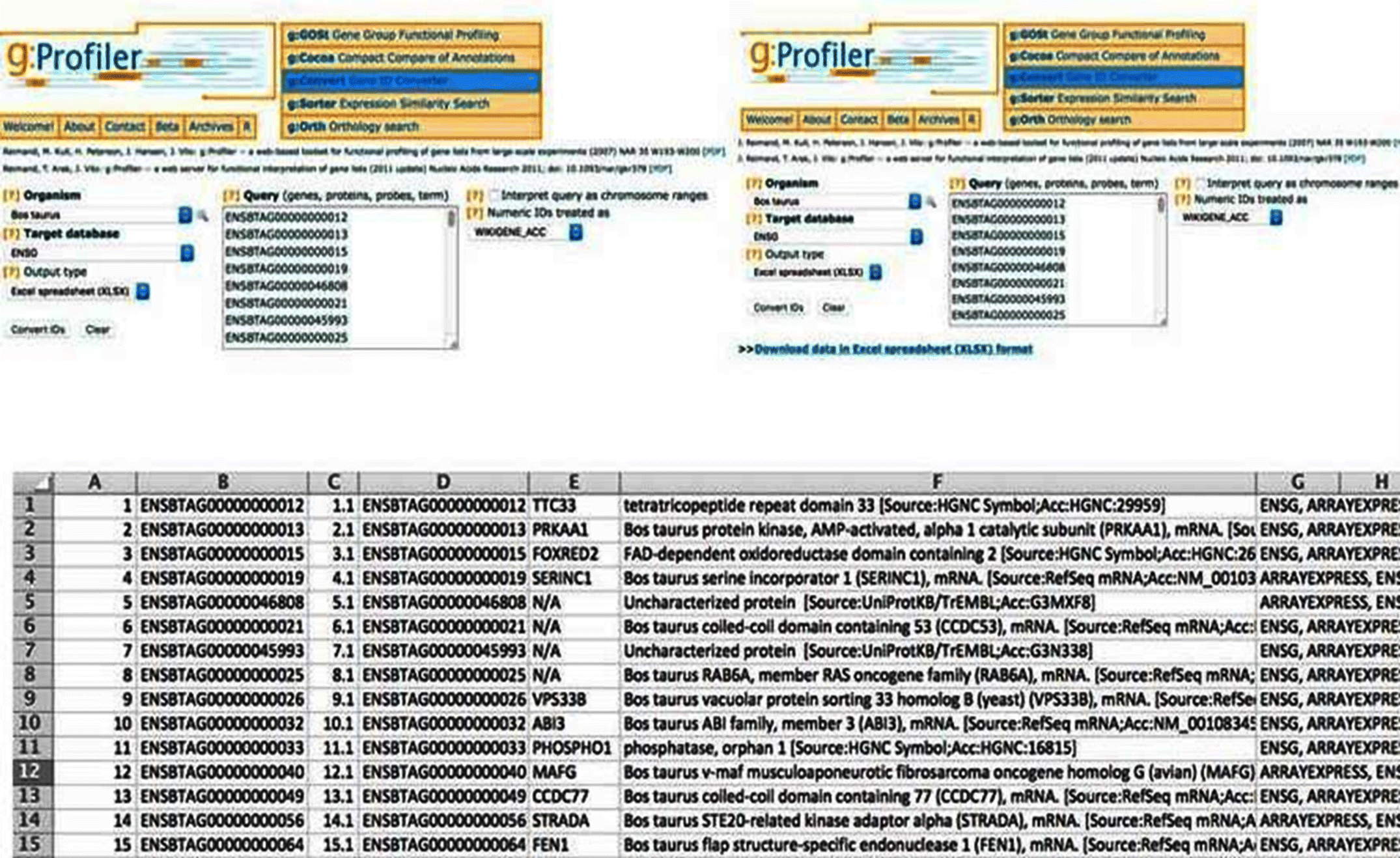
FIGURE 43.2
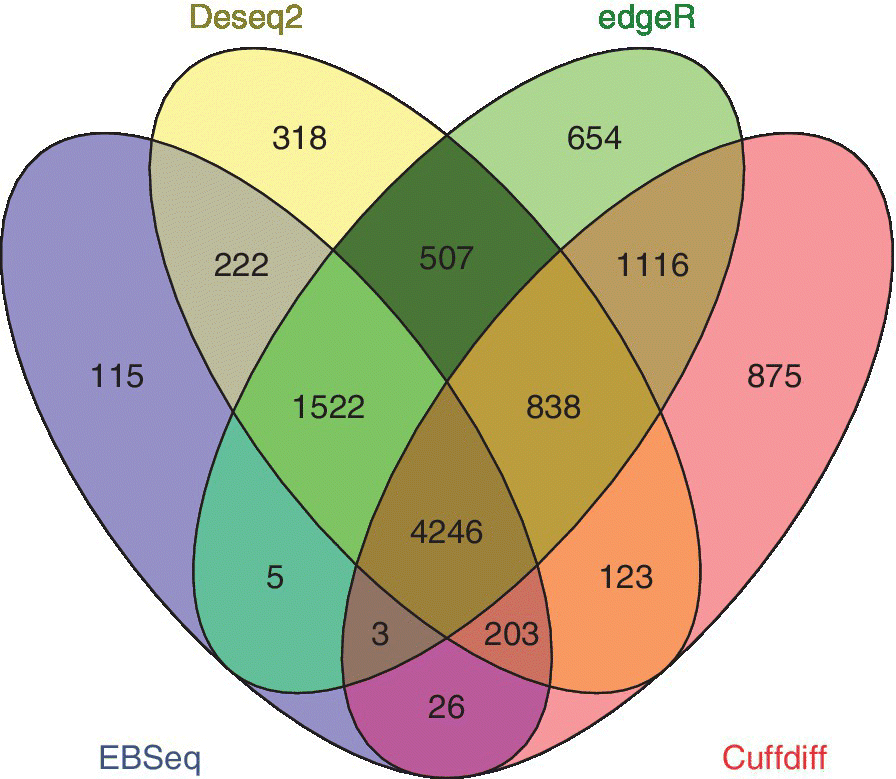
FIGURE 43.3
A total of 4246 commonly differentially expressed genes have been identified by all the packages in our analysis.
43.2 FUNCTIONAL ANNOTATION
Functional annotation is used to determine the gene ontology terms enriched in common differentially expressed genes. Gene ontology (GO) (Ashburner et al., 2000) is an in silico approach to amalgamate the methods of presenting the genes and gene product attributes over divergent species. Gene products are categorized into three categories (biological ...
Get Basic Applied Bioinformatics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

