Chapter 4. Promoting Change And Encouraging Adaptability
COMPETENCIES
Using Power Ethically and Effectively
Championing and Selling New Ideas
Fueling and Fostering Innovation
Negotiating Agreement and Commitment
Implementing and Sustaining Change
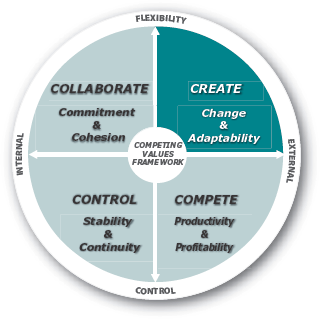
Organizations do not exist in a vacuum. They operate in a complex world that is constantly changing. In contrast to the internal process model, which seeks to buffer the organization from the environment by implementing a system of tight control, the open systems model accepts the need for flexibility and creativity.
Organizational Goals. The core assumption of the open systems model is that continual adaptation and innovation are necessary to acquire the external resources needed by the organization to be successful. As a result, the goals associated with the open systems model are focused on adapting to changes in the environment, rather than on resisting changes. Consistent with the Create action imperative, key activities associated with the open systems quadrant tend to focus on obtaining external support through political adaptation and creative problem solving.
Paradoxes. In our discussion of power and influence, we encounter a key leadership paradox: people yearn for powerful leaders and also distrust powerful leaders. We also consider how successful creative endeavors and innovations often depend more on habit than on spontaneity and why ...
Get Becoming a Master Manager: A Competing Values Approach, Fifth Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

