12Broadband in Gas Line (BIG)
12.1 Introduction to BIG
Broadband in gas line (BIG) has been proposed as an alternative broadband access technology using natural gas pipelines as a microwave waveguide from a network access node to customer's homes and businesses. To a large degree, the BIG access architecture would be similar to coaxial cable systems. Both BIG and coaxial cables have a hundreds of homes and businesses sharing access to a common transmission medium connecting to a network access node. In the United States, natural gas lines serve 63 million residential customers and more than five million commercial enterprises [1]. There is no known deployed service using BIG technology, and it is not clear if any field trials have been conducted.
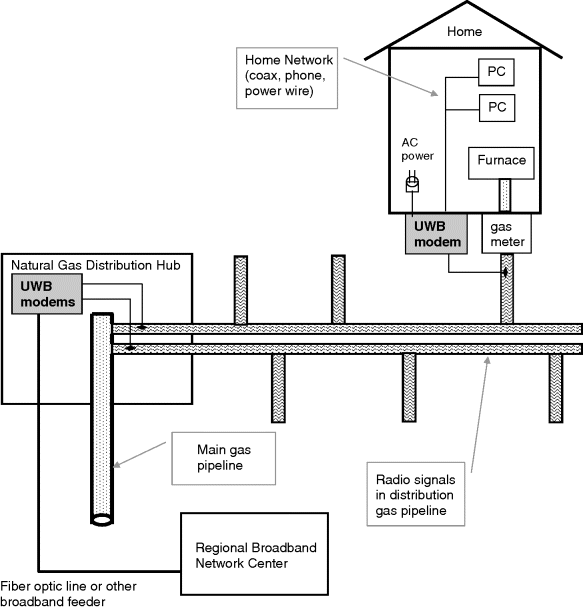
Figure 12.1 BIG access architecture
12.2 Proposed Technology
The leading proponent of BIG technology is the StartUp company Nethercomm Corp. In theory, natural gas pipelines would provide an existing low-loss, low-noise, multi-drop radio waveguide to customers. Ultra-wideband radio technology has been proposed for BIG. The claimed media bit-rate capacity is approximately five to ten Gbps (probably combined upstream plus downstream) over a distance of ten kilometers or more. Like coaxial cable, this media bit-rate capacity would be shared by all customers connected to a distribution line. With a typical number of customers per line, ...
Get Broadband Access: Wireline and Wireless - Alternatives for Internet Services now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

