Chapter 4. DATA LINK LAYER
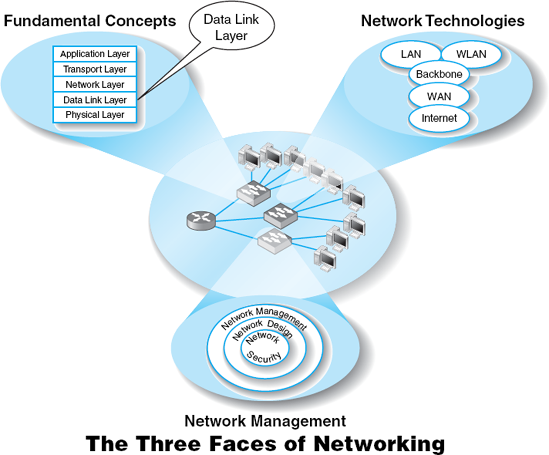
THE DATA link layer (also called layer 2) is responsible for moving a message from one computer or network device to the next computer or network device in the overall path from sender or receiver. It controls the way messages are sent on the physical media. Both the sender and receiver have to agree on the rules or protocols that govern how they will communicate with each other. A data link protocol determines who can transmit at what time, where a message begins and ends, and how a receiver recognizes and corrects a transmission error. In this chapter, we discuss these processes, as well as several important sources of errors.
OBJECTIVES ▾
Understand the role of the data link layer
Become familiar with two basic approaches to controlling access to the media
Become familiar with common sources of error and their prevention
Understand three common error detection and correction methods
Become familiar with several commonly used data link protocols
CHAPTER OUTLINE ▾
INTRODUCTION
MEDIA ACCESS CONTROL
Controlled Access
Contention
Relative Performance
ERROR CONTROL
Sources of Errors
Error Prevention
Error Detection
Error Correction via Retransmission
Forward Error Correction
Error Control in Practice
DATA LINK PROTOCOLS
Asynchronous Transmission
Synchronous Transmission
TRANSMISSION EFFICIENCY
IMPLICATIONS FOR MANAGEMENT
SUMMARY
INTRODUCTION
In Chapter 1, we introduced the concept of ...
Get Business Data Communications and Networking now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

