2
Detection and Classification
Pattern classification is the act of assigning a class label to an object, a physical process or an event. The assignment is always based on measurements that are obtained from that object (or process, or event). The measurements are made available by a sensory system. See Figure 2.1. Table 2.1 provides some examples of application fields in which classification is the essential task.
The definition of the set of relevant classes in a given application is in some cases given by the nature of the application, but in other cases the definition is not trivial. In the application ‘character reading for license plate recognition’, the choice of the classes does not need much discussion. However, in the application ‘sorting tomatoes into “class A”, “class B”, and “class C”’ the definition of the classes is open for discussion. In such cases, the classes are defined by a generally agreed convention that the object is qualified according to the values of some attributes of the object, e.g. its size, shape and colour.
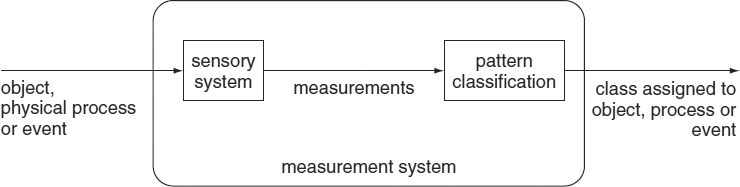
Figure 2.1 Pattern classification
Table 2.1 Some application fields of pattern classification
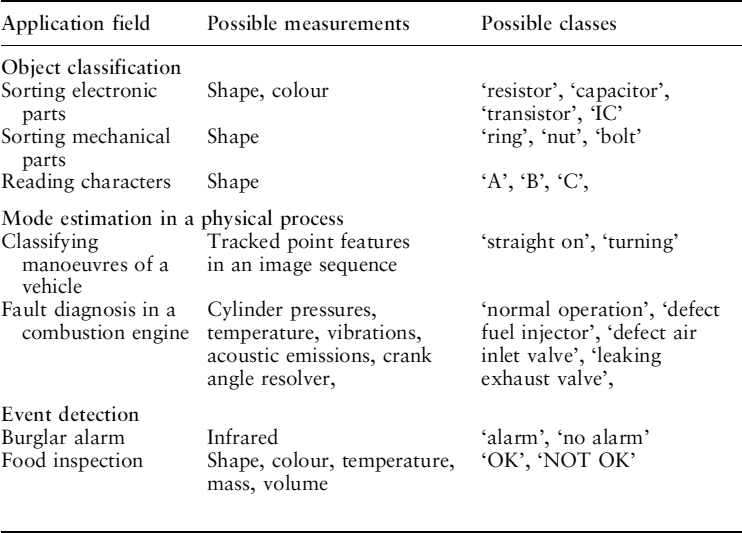
The sensory system measures some physical properties of the object that, hopefully, are relevant for classification. This chapter is confined to the simple ...
Get Classification, Parameter Estimation and State Estimation: An Engineering Approach Using MATLAB now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

