3Detection and Classification
Pattern classification is the act of assigning a class label to an object, a physical process or an event. The assignment is always based on measurements that are obtained from that object (or process, or event). The measurements are made available by a sensory system (see Figure 3.1). Table 3.1 provides some examples of application fields in which classification is the essential task.
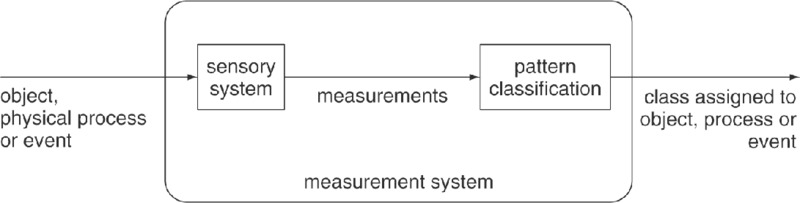
Figure 3.1 Pattern classification.
Table 3.1 Some application fields of pattern classification
| Possible | ||
| Application field | measurements | Possible classes |
| Object classification | ||
| Sorting electronic parts | Shape, colour | ‘resistor’, ‘capacitor’, ‘transistor’, ‘IC’ |
| Sorting mechanical parts | Shape | ‘ring’, ‘nut’, ‘bolt’ |
| Reading characters | Shape | ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’ |
| Mode estimation in a physical process | ||
| Classifying manoeuvres of a vehicle | Tracked point features in an image sequence | ‘straight on’, ‘turning’ |
| Fault diagnosis in a combustion engine | Cylinder pressures, temperature, vibrations, acoustic emissions, crank angle resolver | ‘normal operation’, ‘defect fuel injector’, ‘defect air inlet valve’, ‘leaking exhaust valve’, |
| Event detection | ||
| Burglar alarm | Infrared | ‘alarm’, ‘no alarm’ |
| Food inspection | Shape, colour, temperature, mass, volume | ‘OK’, ‘NOT OK’ |
The definition of the set of relevant classes in a given application is in some cases given by ...
Get Classification, Parameter Estimation and State Estimation, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

