2.3 CRIBBING
The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology gives to steal and to pilfer as definitions of the Shakespearian verb to crib. The term cribbing in cryptography refers to the process of inferring key and plaintext from ciphertext based on partial knowledge of the plaintext. A crib is a word or phrase w = (w0, w1, …, wM−1) known (or assumed) to appear in the plaintext. Partial knowledge of the plaintext is a reasonable assumption:
- Letters usually contain stereotyped beginnings and/or endings: Dear …, Sincerely yours, Att:, Senator …;
- Message transmitted over a network have special formats; and
- Files are often highly structured, records divided into fields containing data with known characteristics.
When the crib w = (w0, w1, …, wM − l) occurs in the plaintext x, certain strings of letters derived from w will also occur in the ciphertext y = TN, τ(x).
If N ≥ M, then w determines N subcribs, which are all the maximal length strings ![]() ≡ {S0, S1, …, Sn−1} formed by the letters in w, which are pairwise-separated by exactly N positions.
≡ {S0, S1, …, Sn−1} formed by the letters in w, which are pairwise-separated by exactly N positions.
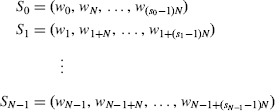
where si will denote the length of Si
The cryptanalysis of columnar transposition by cribbing is based on the following result.
Proposition 2.1: If x → y = TN, τ (x), then
| 2.1a | Pairs of letters (xt, xt+N) in the plaintext separated by N places ... |
Get Computer Security and Cryptography now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

