3.7 THE HIDDEN MARKOV MODEL (HMM)
A class of stochastic processes now referred to as Hidden Markov models (HMM) are described in the two important papers published by Petrie [1969] and Baum et al. [1969]. The application of HMM to automatic speech recognition (ASR) was quickly recognized, and is detailed in the survey papers by Levinson et al. [1983], Rabiner and Juang [1986] and Poritz [1988]. We outline the main ideas and show how HMM may be applied to cryptanalyze a monoalphabetic substitution.
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a two-stage random process; both the input X = (X0, X1,…, Xn) and output states Y = (Y0, Y1,…, Yn) consists of integers in ![]() . The HMM is constructed from
. The HMM is constructed from
- A Markov chain with parameters (π, P) generating (hidden) states X
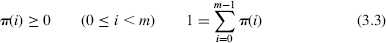
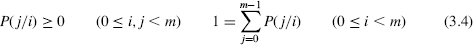
- An output probability distribution q(j/i) = Pr{Yt = j/Xt = i} for each hidden state i
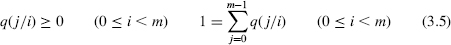
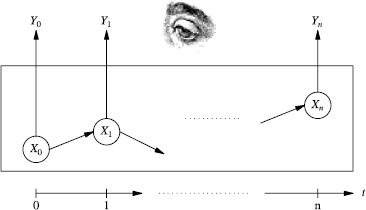
Figure 3.3 Observing the hidden states.
The evolution of the HMM may be described as follows:
- The initial hidden state X0 = x0 is chosen with probability ...
Get Computer Security and Cryptography now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

