2
Chip Basics: Time, Area, Power, Reliability, and Configurability
2.1 INTRODUCTION
The trade-off between cost and performance is fundamental to any system design. Different designs result either from the selection of different points on the cost–performance continuum or from differing assumptions about the nature of cost or performance.
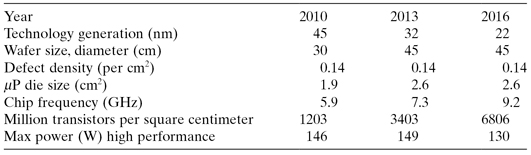
The driving force in design innovation is the rapid advance in technology. The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) regularly makes projections, called the SIA road map, of technology advances, which become the basis and assumptions for new chip designs. While the projections change, the advance has been and is expected to continue to be formidable. Table 2.1 is a summary of the roadmap projections for the microprocessors with the highest performance introduced in a particular year [133]. With the advances in lithography, the transistors are getting smaller. The minimum width of the transistor gates is defined by the process technology. Table 2.1 refers to process technology generations in terms of nanometers; older generations are referred to in terms of microns (µm). So the previous generations are 65 and 90 nm, and 0.13 and 0.18 µm.
TABLE 2.1 Technology Roadmap Projections
2.1.1 Design Trade-Offs
With increases in chip frequency and especially in transistor density, the designer must be able to find the best set of trade-offs in an environment ...

