Chapter 11. Partial Differential Equations
11.1 Introduction
11.2 Poisson's Equation
11.3 Laplace's Equation
11.4 Heat Equation
11.5 Wave Equation
11.6 Visual Solution: Code11
11.7 Summary
Numerical Exercises
Programming Challenges
INTRODUCTION
Partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation that has one or more partial derivatives as independent variables in its terms. Some typical examples are
Equation 11.1.
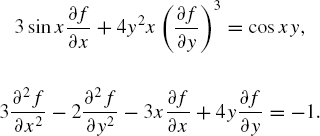
The order of a partial differential equation is defined as the highest partial derivative of the terms in the equation. Therefore, the first example above is the first-order PDE, whereas the second is the second-order PDE. The degree of a partial differential equation is defined as the power of the highest derivative term in the equation. It can be verified from the definition that the two equations above have the degrees of three and one, respectively.
In general, a partial differential equation of order n having m variables x i for i = 1, 2,..., m is expressed as
Equation 11.1.
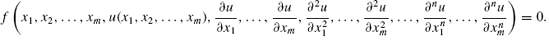
In the above equation,
In this chapter, we will concentrate on numerical problems involving second-order partial differential equations only. A second-order partial differential equation with variables x1, x2, and ...
Get Computing for Numerical Methods Using Visual C++ now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

