8.2. DISTRIBUTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EQUITY MULTIPLES
In Chapter 7, we noted that most multiples have distributions that are skewed toward positive values and that the distributions themselves are volatile and change over time. Equity multiples are no exception to this general rule. In this section, we examine the distributions of some widely used equity multiples.
8.2.1. Price-Earnings Ratio
The price-earnings ratio is the ratio of the market value of equity to the earnings generated for equity investors:
While it is conventionally computed using the current price price per share and diluted earnings per share, the alternative measures of market equity—aggregate value of equity, equity net of cash, and option-augmented equity—can be used with the consistent measure of earnings (see Table 8.1). Figure 8.1 presents the distribution of P/E ratios for U.S. stocks in January 2006. The current P/E, trailing P/E, and forward P/E ratios are all shown in this figure.
Figure 8.1. P/E Ratios—U.S. Stocks in January 2006
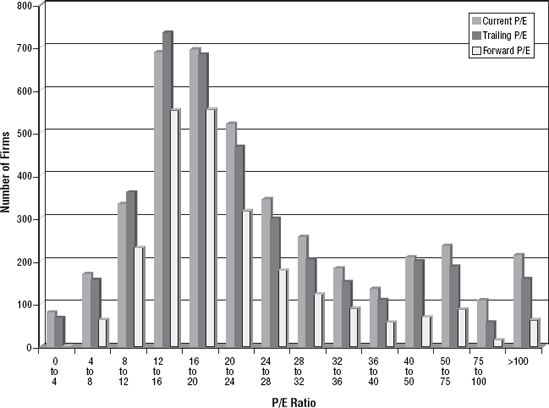
Table 8.3 presents summary statistics, in January 2006, on all three measures of the price-earnings ratio, starting with the mean and the standard error, and including the median, 10th, and 90th percentile values.[]
[] The mean and the standard deviation are the summary ...
Get Damodaran on Valuation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

