6
Knock-in/Out Margrabe*
with Jørgen Haug
In this chapter we push the Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) formula to the limit by using it to value exchange-one-asset-for-another options with knock-in or knock-out provisions that depend on the ratio of the two asset prices. These option contracts are relevant to investors and traders concerned with the relative performance of securities, and they crop up in M&As.
1 Margrabe Options
Exchange-one-asset-for-another options give the owner the right to exchange asset S2 for asset S1 at expiration and were originally analyzed by Margrabe (1978).1 The payoff from such a call option is
![]()
where (·)+ is the positive part. Margrabe considered the special case when the two asset prices follow geometric Brownian motion:
![]()
where μi and σi are the instantaneous return and volatility of asset i = 1, 2, and dz1 and dz2 are correlated Wiener processes with correlation coefficient ρ. The price of a call option with τ years left to maturity, derived in the appendix as a prelude to extensions with barriers, is then
![]()
where
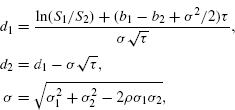
and bi is the cost of carry of asset i = 1, ...
Get Derivatives Models on Models now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

