3
Linear Differential Equations with Constant Coefficients
3.1 INTRODUCTION
In the previous chapter, we have studied the linear differential equation of the first order
It is called a homogeneous (or reduced) equation if Q(x) ≡ 0 and a non-homogeneous equation if Q(x) ≢ 0.
If we substitute y = u + v in Eq. (3.1), we have
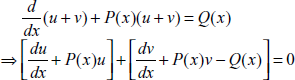
which is satisfied if
This shows that y = u + v is the general solution (or complete solution) of Eq. ...
Get Differential Equations now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

