1
Induction Machine
The three-phase induction machine with non-salient poles is the most widespread electric motor because of its simple and robust construction; it is perhaps the electrical machine that has the least intuitive operation (Caron and Hautier, 1995). It has been the subject of very many technical publications.
1.1 Electrical Equations and Equivalent Circuits
Starting from the equivalent three-phase electrical circuit of the induction machine without neutral current, let us establish initially the relations between the various electrical variables.
1.1.1 Definitions and Notation
Definitions and notation of motor parameters:
| Rs |
| Rr |
| ls |
| lr |
| Lm |
| Ls = Lm + ls |
| Lr = Lm + lr |
| 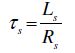 |
| 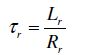 |
| Np |
| 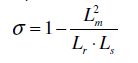 |
Definitions and notations of mechanical and electrical angular frequencies:
- mechanical angular frequency of the rotor Ω
- polar mechanical angular frequency1 ω = Np ⋅ Ω
- stator electrical angular frequency ωs
- rotor electrical angular frequency ωr
- relative slip ...
Get Direct Eigen Control for Induction Machines and Synchronous Motors now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

