3.3. Spectral representation of a WSS process
In this section we explain the steps enabling us to arrive at the spectral representation of a process. In order not to obscure these steps, the demonstrations of the results which are quite long without being difficult are not given.
3.3.1. Problem
The object of spectral representation is:
1) To study the integrals (called Wiener integrals) of the ![]() type obtained as limits, in a meaning to clarify the expressions with the form:
type obtained as limits, in a meaning to clarify the expressions with the form:
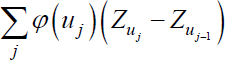
where S is a restricted interval of ![]() , φ is a mapping with complex values (and other conditions), ZS = {Zu | u ∈ S} is a 2nd order process with orthogonal increments (abbreviated as p.o.i.) whose definition will be given in what follows.
, φ is a mapping with complex values (and other conditions), ZS = {Zu | u ∈ S} is a 2nd order process with orthogonal increments (abbreviated as p.o.i.) whose definition will be given in what follows.
2) The construction of the Wiener integral being carried out, to show that reciprocally, if we allow ourselves a WSS process X![]() θ, we can find a p.o.i.
θ, we can find a p.o.i. 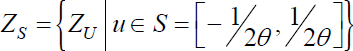 such that ∀j ∈
such that ∀j ∈ ![]() Xjθ may be written ...
Xjθ may be written ...
Get Discrete Stochastic Processes and Optimal Filtering now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

