Chapter 2. Resistors
2.0 Introduction
Resistors are used in almost every electronic circuit, come in a huge variety of shapes and sizes, and are available in a range of values that spans milliohms (thousandths of an ohm) to mega ohms (millions of ohms).
Ohm, the unit of resistance, is usually abbreviated as the Greek letter omega (Ω), although you will sometimes see the letter R used instead. For example, 100Ω and 100R both mean a resistor with a resistance of 100 ohms.
2.1 Read Resistor Packages
Problem
You want to work out the value of a resistor.
Solution
On a through-hole resistor (a resistor with leads) that has colored stripes on it, use the resistor color code.
If your resistor has stripes in the same positions as Figure 2-1 then the three stripes together on the left determine the resistor’s value and the single stripe on the right determines the accuracy of the value.
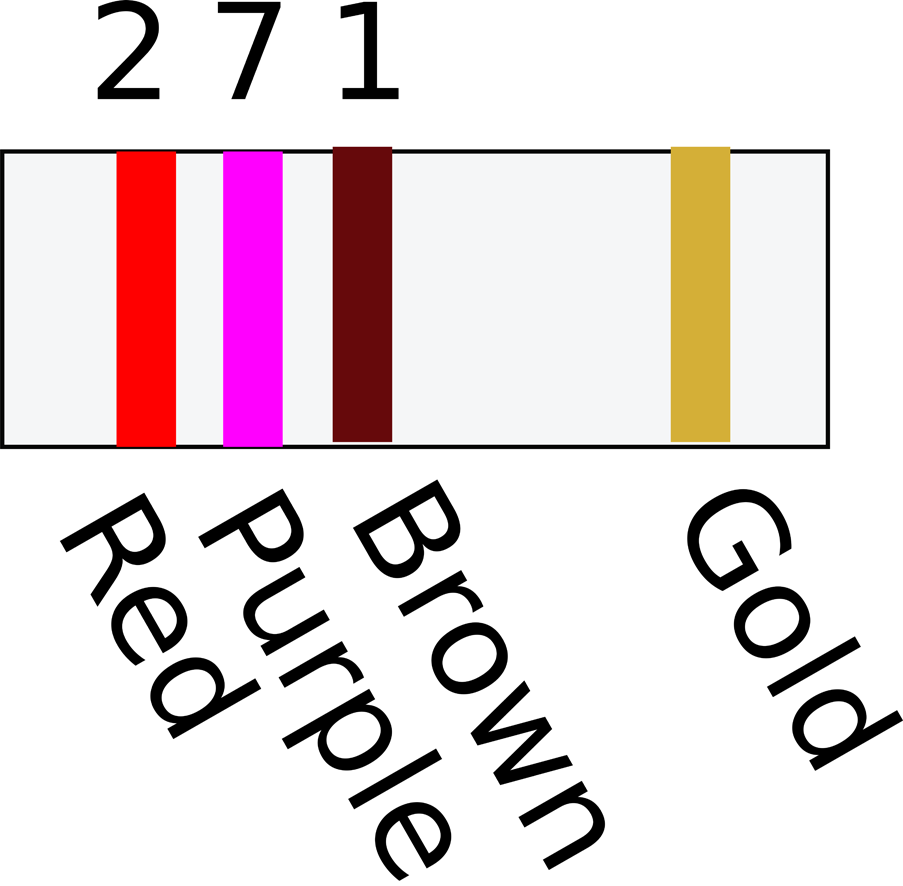
Figure 2-1. A Three-Stripe Resistor
Each color has a value as listed in Table 2-1.
|
Black |
0 |
|
Brown |
1 |
|
Red |
2 |
|
Orange |
3 |
|
Yellow |
4 |
|
Green |
5 |
|
Blue |
6 |
|
Violet |
7 |
|
Gray |
8 |
|
White |
9 |
|
Gold |
1/10 |
|
Silver |
1/100 |
For a three-stripe resistor such as this, the first two stripes determine the basic value (say 27 in Figure 2-1) and the third stripe determines the number of zeros to add to the end. In the example of Figure 2-1 ...
Get Electronics Cookbook now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

