Geometrically, if di is the vertical distance from the data point (xi, yi) to the point (xi, a+bxi) on the line, then di = yi – a – bxi (see Figure 26.4). We must minimize the sum of the squares of the vertical distances di, that is, the sum ![]()
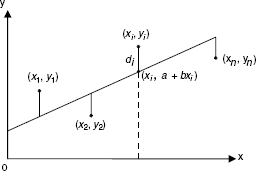
Figure 15.4
To minimize e (a,b), we equate to zero the partial derivatives of (63) with respect to ‘a’ and ‘b’. Thus
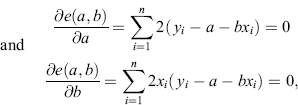
which are known as normal equations. We write these equations in the form ...
Get Engineering Mathematics, Volume II, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

