88 Equivalence and Noninferiority Tests
Computational considerations:
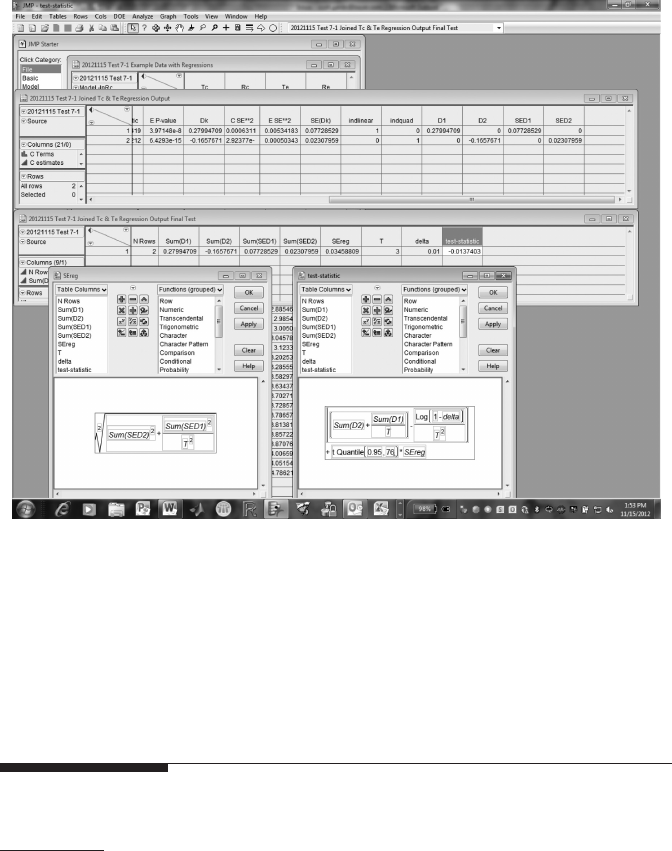
Computationally, Test 7.1 is a combination of Test 2.5 (regression slope) and
Test 2.2 (comparison of two means, xed Δ). In the example used here, the
two systems are considered equivalent at time T = 3 if the reliability of the
evaluation system, Re(T), is at least 99 percent of Rc(T) (i.e., δ = 0.01).
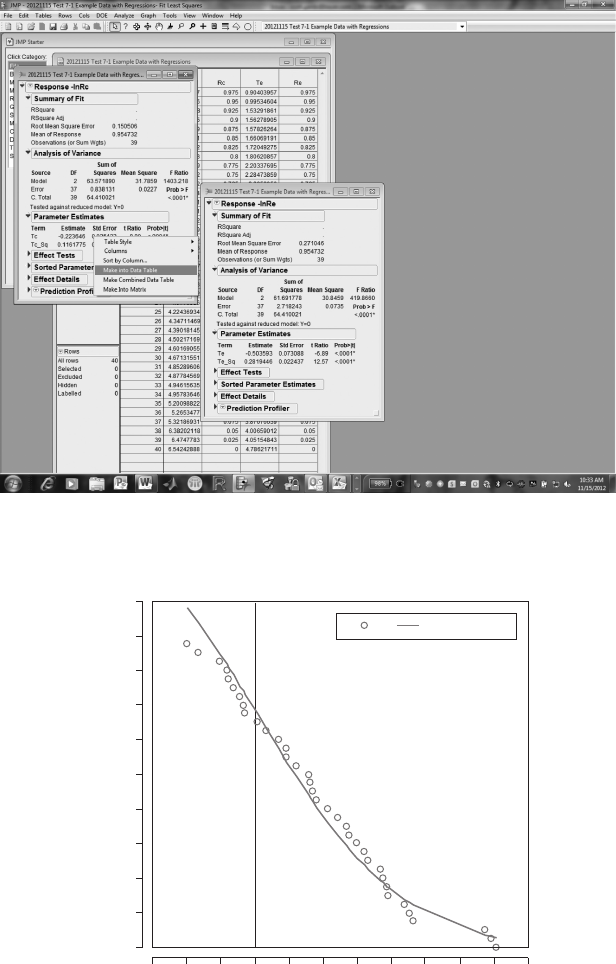
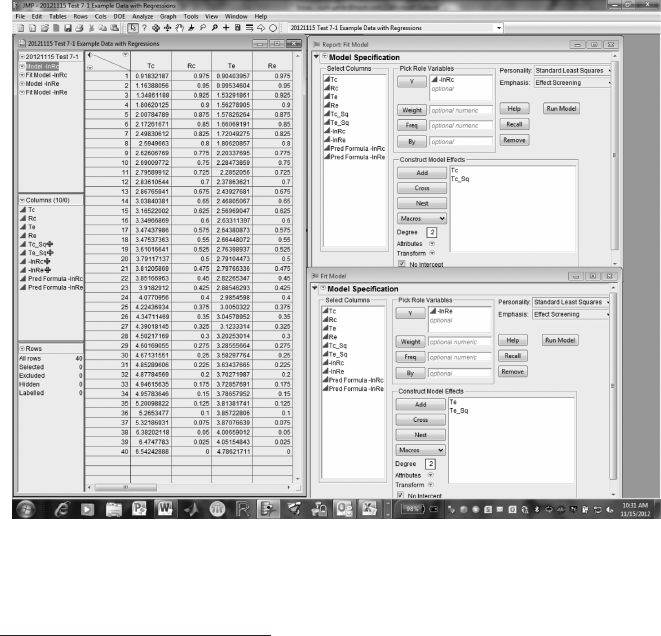
JMP Data Table and formulas (Figure 7.2 and Figure 7.3). The columns
reandrc in Figure7.2 represent the reliability functions for the time-to-event
variables, Te and Tc. You can use the “Fit Model” function to obtain coef-
cient estimates. Make sure to check the “No Intercept” option box.
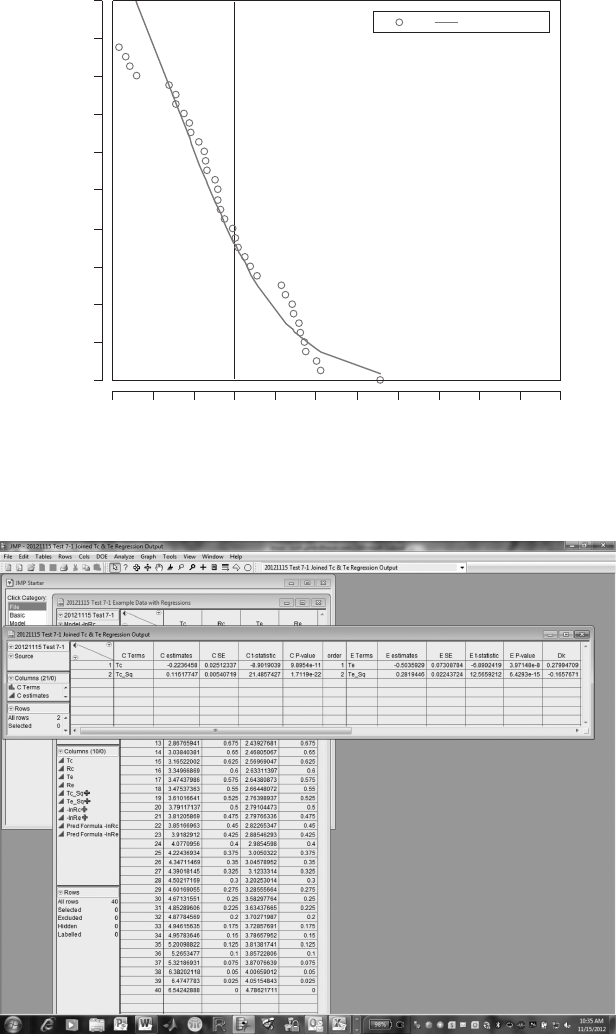
Right-click on the Parameter Estimates Chapter of the Fit Model output,
and select the “Make into Data Table” option. Create new columns to com-
pute the standard error squared, and a column that indicates the row num-
ber in each parameter estimate table (called “order” in this example). Join the
tables for Te and Tc parameter estimates using the Tables -> Join function,
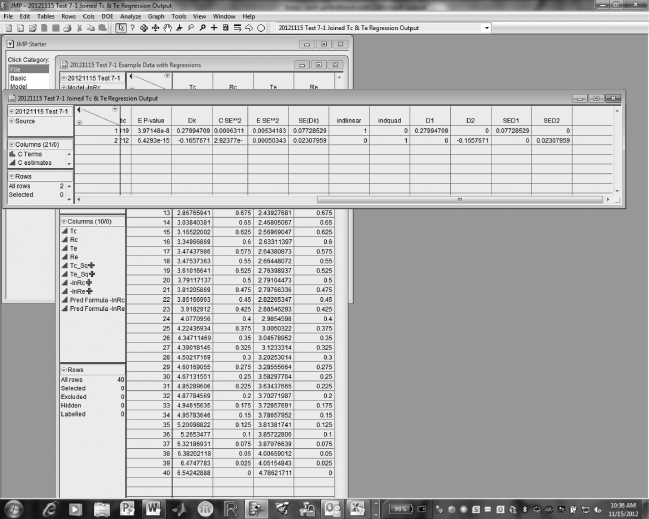
with “order” as the matching column. Then compute Dk, the difference in
the parameter estimates, for the linear (order = 1) and quadratic (order = 2)
terms of the two models.
• The models and the data (Figures7.4 and 7.5):
FIGURE 7.2
Test 7.1, JMP screen 1.