12Plastics Processing
12.1 Introduction
This chapter is concerned with the manufacturing processes used for making plastic components. Plastic materials were discussed in section Chapter 6, where their importance to modern technology was also noted, and the production of plastic was described in Chapter 7.
One of the major advantages of plastics is that, by choosing a suitable moulding or forming process, a complete component can be produced that requires little or no finishing operations. As the number of options available to the engineer when selecting the process is large, the optimum will be found only by considering the advantages and limitations of each process, the design of the component to be made, the tool or mould design and the processing characteristics of the plastic being used. A few of the main thermoplastic moulding and forming processes are now explained.
12.2 Extrusion
This is a continuous process in which one or more Archimedean feeder screws are mounted within a cylinder as shown in Figure 12.1. This cylinder is heated and as the screws rotate they plasticise and convey the plastic along their threads from the feeder hopper to a die. The section of this die determines the cross sectional shape of the extrusion. Extrusion machines come in a range of sizes with screws ranging in diameter from 25 to 200 mm.
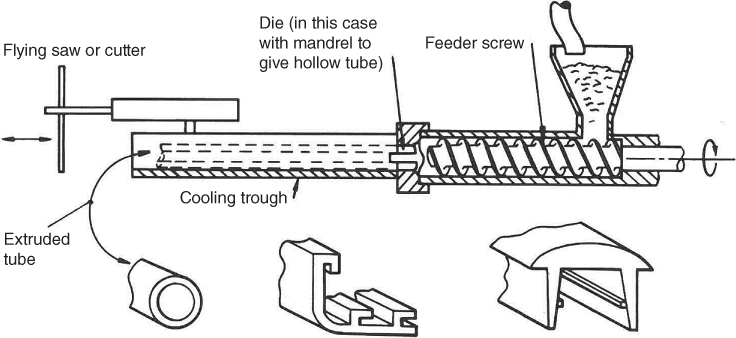
Figure 12.1 The polymer extrusion process and typical ...
Get Essential Manufacturing now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

