Appendix C. Complex Numbers
Each complex number z is a point in the complex plane, which is spanned by the real axis and the imaginary axes:
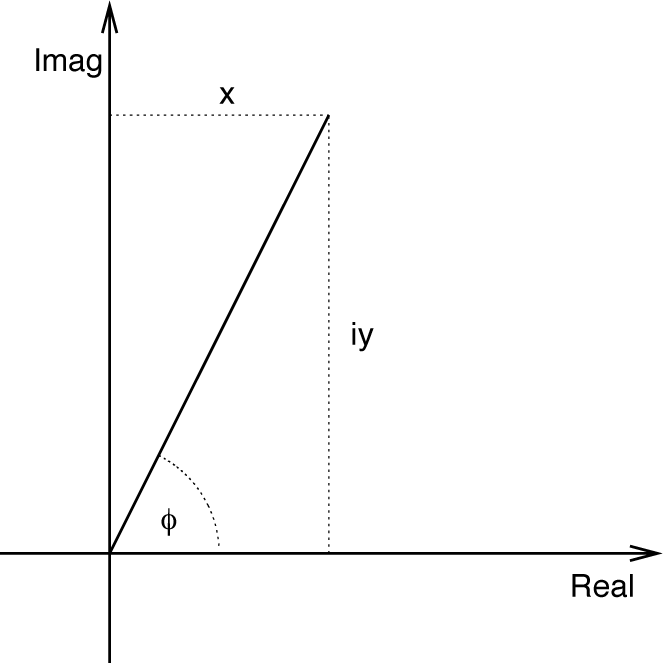
Two coordinate systems are commonly used for a (two-dimensional) plane: Cartesian and polar coordinates. For every complex number there exist two equivalent representations:
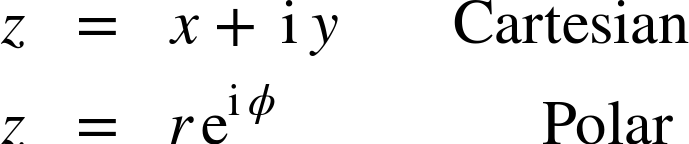
Here

is the “imaginary unit.”
We can transform between those representations as follows:
|
| Real part |
|
| Imaginary part |
|
| Magnitude |
|
| Phase |
Basic Operations
Complex numbers are added and multiplied component by component while taking into account that i2 = –1. If z1 = x1 + iy1 and z2 = x2 + iy2, then
Each complex number z has a “complex conjugate,” denoted , which is the same as except that the sign ...
Get Feedback Control for Computer Systems now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

