Chapter 2. Database and Data Management
If you’re planning to use Hadoop, it’s likely that you’ll be managing lots of data, and in addition to MapReduce jobs, you may need some kind of database. Since the advent of Google’s BigTable, Hadoop has an interest in the management of data. While there are some relational SQL databases or SQL interfaces to HDFS data, like Hive, much data management in Hadoop uses non-SQL techniques to store and access data. The NoSQL Archive lists more than 150 NoSQL databases that are then classified as:
-
Column stores
-
Document stores
-
Key-value/tuple stores
-
Graph databases
-
Multimodel databases
-
Object databases
-
Grid and cloud databases
-
Multivalue databases
-
Tabular stores
-
Others
NoSQL databases generally do not support relational join operations, complex transactions, or foreign-key constraints common in relational systems but generally scale better to large amounts of data. You’ll have to decide what works best for your datasets and the information you wish to extract from them. It’s quite possible that you’ll be using more than one.
This book will look at many of the leading examples in each section, but the focus will be on the two major categories: key-value stores and document stores (illustrated in Figure 2-1).
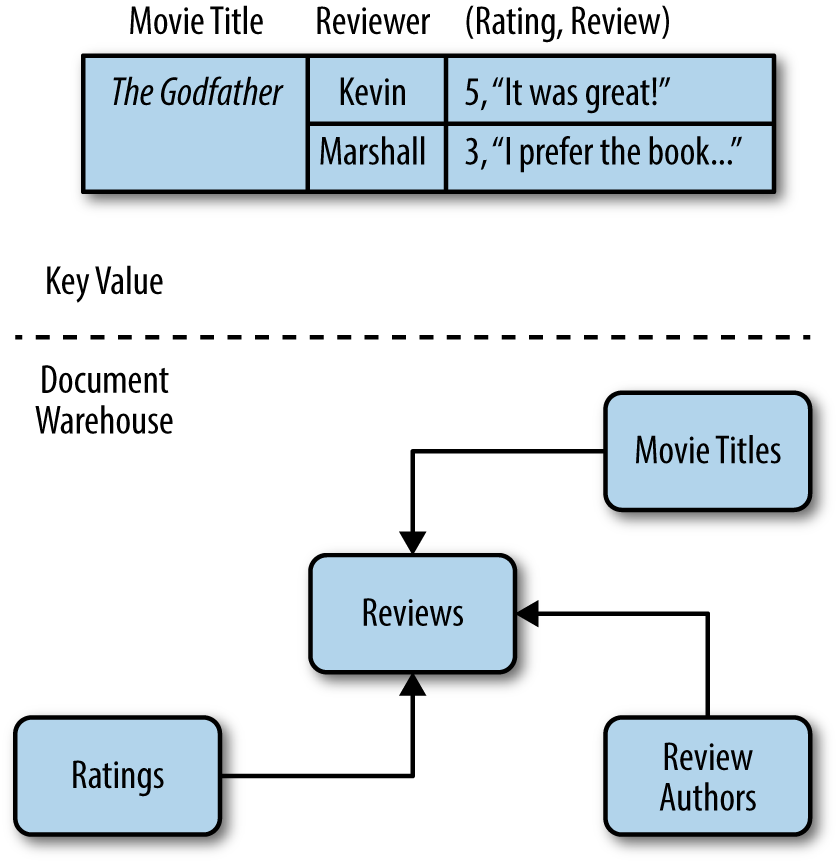
Figure 2-1. Two approaches to indexing
A key-value store can be thought of like a catalog. All the items in a catalog ...
Get Field Guide to Hadoop now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

