CHAPTER 13
The Complete Income Statement
Key Points
The following key points are emphasized in this chapter:
- Economic consequences associated with reporting net income.
- Two different concepts of income: matching and fair market value.
- A framework for financing, investing, and operating transactions.
- Categories that constitute a complete income statement and how they provide measures of income that address the objectives of financial reporting.
- Intraperiod tax allocation.
- Earnings per share disclosure on the income statement.
The income statement from pharmaceutical giant Merck's 2012 annual report follows (dollars in billions):
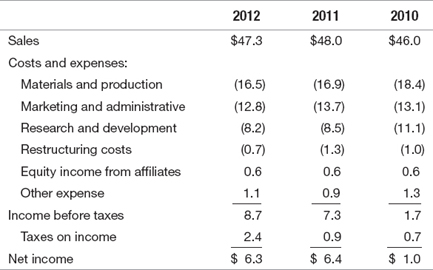
Net income appears to have increased from $1 billion (2010) to $6.3 billion (2012), a very steep upward slope both in terms of raw numbers and as a percentage of sales. Indeed, Merck's future looks rosy! Yet, what about expense and income items like restructuring costs, equity income, and “other” expenses? They have all been included in the net income calculation, but are they part of Merck's core operations, and can they be expected to persist in the future? And taxes—why only $0.7 billion in 2010, but $2.4 billion in 2012? The rules governing income statement disclosure, which are covered in this chapter, are designed to help.
This chapter covers (1) the economic consequences associated with income measurement and disclosure, (2) conceptual issues of ...
Get Financial Accounting in an Economic Context, 9th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

