16.2 Single-Price Monopoly
MyEconLab Concept Video
To understand how a single-price monopoly makes its output and price decisions, we must first study the link between price and marginal revenue.
Price and Marginal Revenue
Because in a monopoly there is only one firm, the demand for the firm’s output is the market demand. Let’s look at Bobbie’s Barbershop, the sole supplier of haircuts in Cairo, Nebraska. The table in Figure 16.2 shows the demand schedule for Bobbie’s haircuts. For example, at $12, consumers demand 4 haircuts an hour (row E).
Figure 16.2
Demand and Marginal Revenue
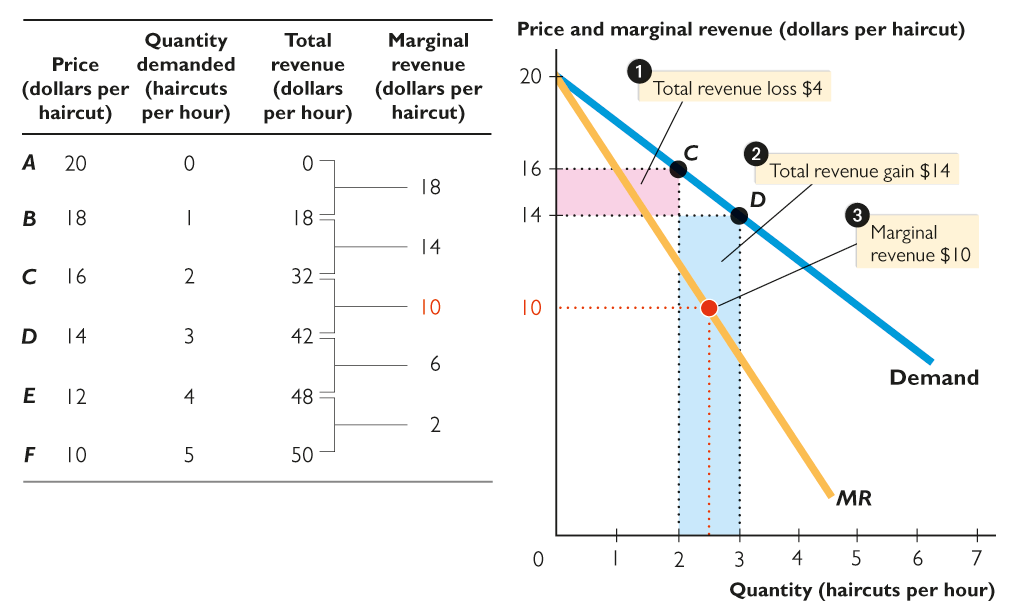
The table shows the market demand schedule for haircuts and ...
Get Foundations of Economics, 8th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

