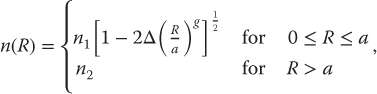6Characterization
Characterization of optical fibers is very important in installing or designing optical fiber communication systems and improving their performance. Numerous measurement methods have been developed to evaluate the various performance indicators or parameters of optical fibers. This chapter explains several such methods selected for the characterization of the optical fibers described in this book and introduces methods of analyzing the obtained data by comparing the experimental results of several representative plastic optical fibers (POFs).
6.1 Refractive Index Profile
The bandwidth of an optical fiber strongly depends on the modal dispersion. The modal dispersion can be controlled by controlling the refractive index profile (RIP), which has a decisive effect on the bandwidth (see Chapter 3) and is a basic and important parameter of optical fibers. The pulse-broadening caused by modal dispersion seriously limits the transmission data rate of multimode fibers (MMFs) because overlapping of the broadened pulses induces intersymbol interference and disturbs correct signal detections, increasing the bit error rate [1].
6.1.1 Power-Law Approximation
A power-law index profile approximation is a well-known method of analyzing the RIP of graded-index (GI) MMFs [2]. In this approximation, the refractive index distribution of a GI MMF is described by
where n(
Get Fundamentals of Plastic Optical Fibers now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.